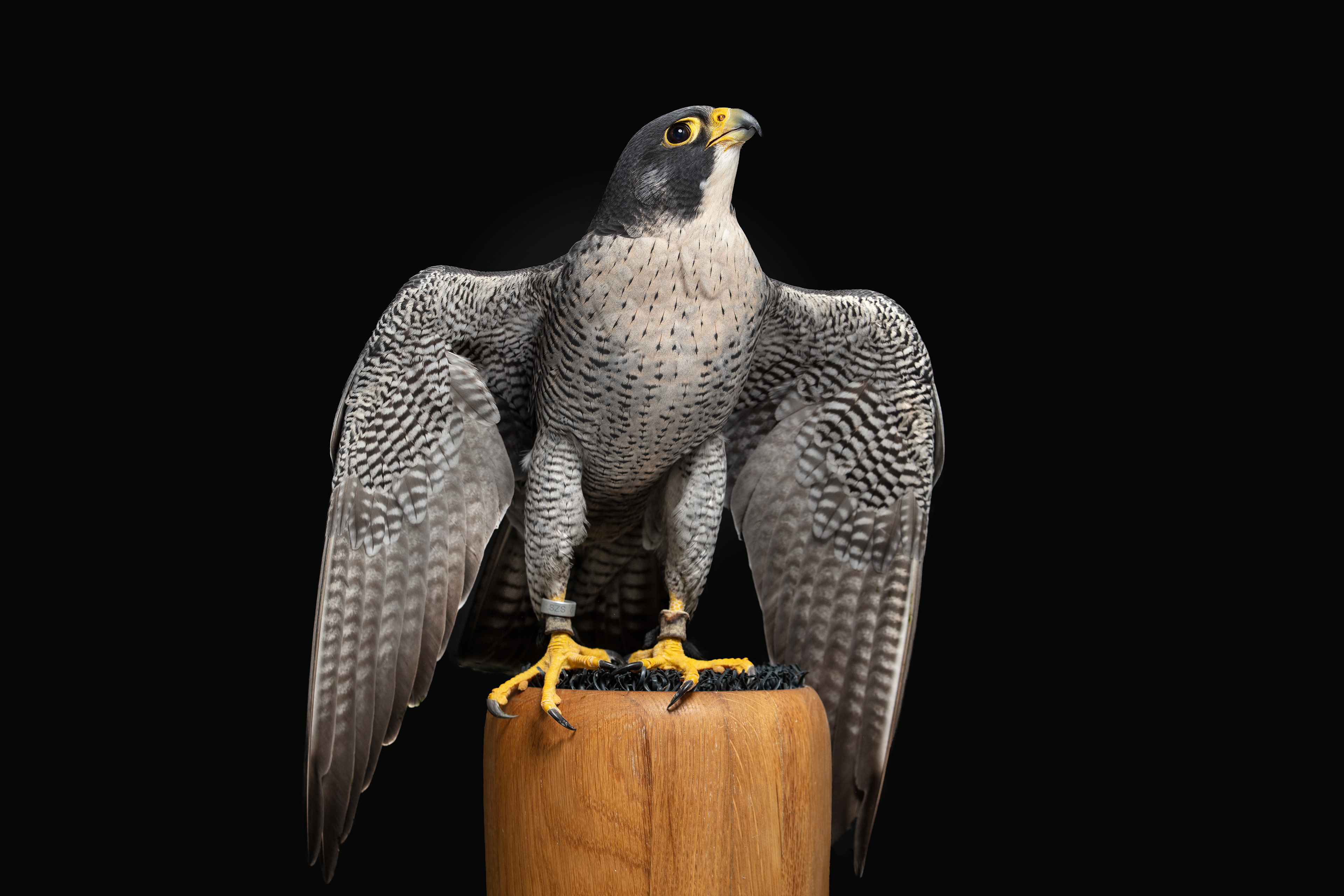
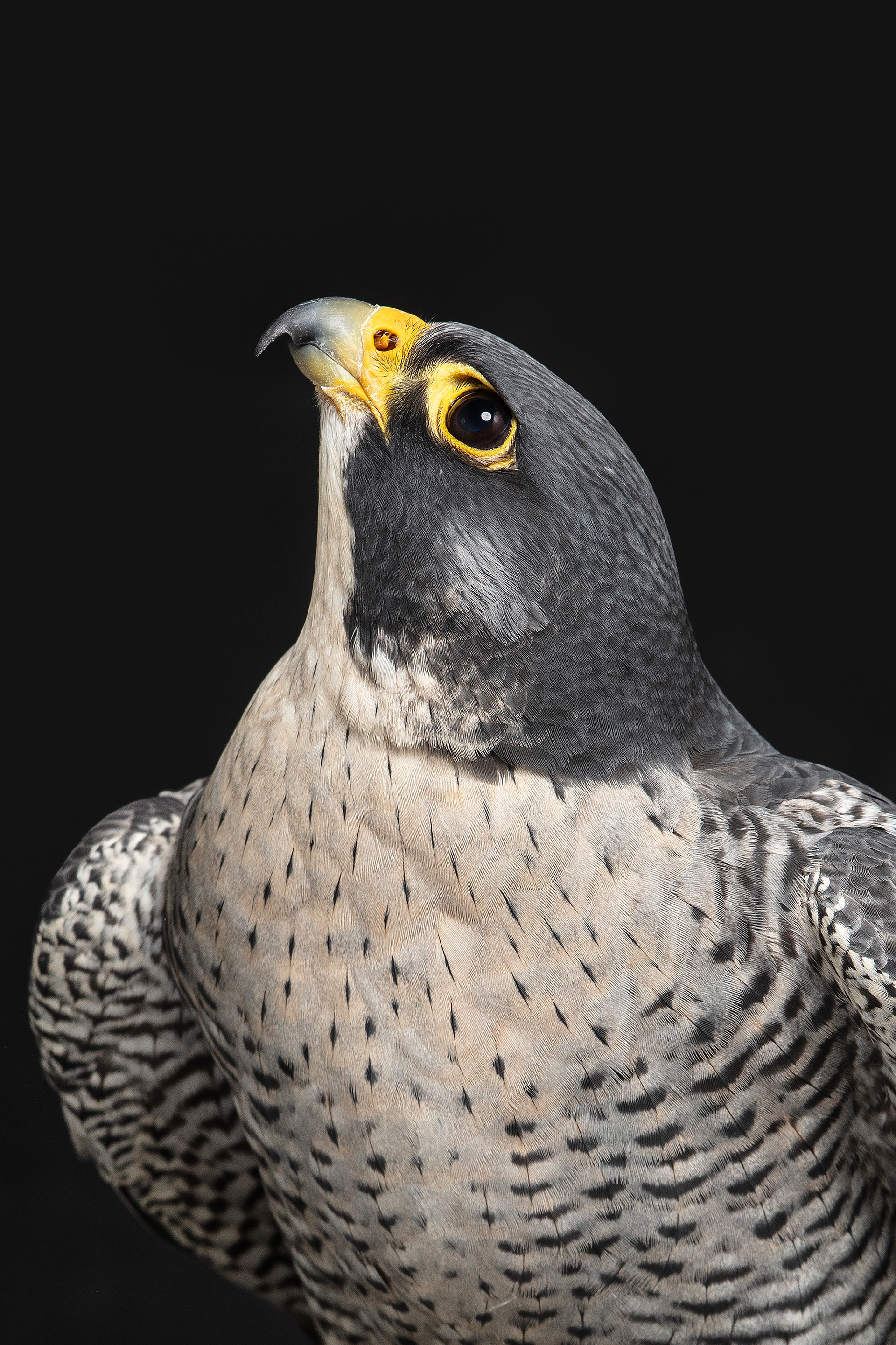
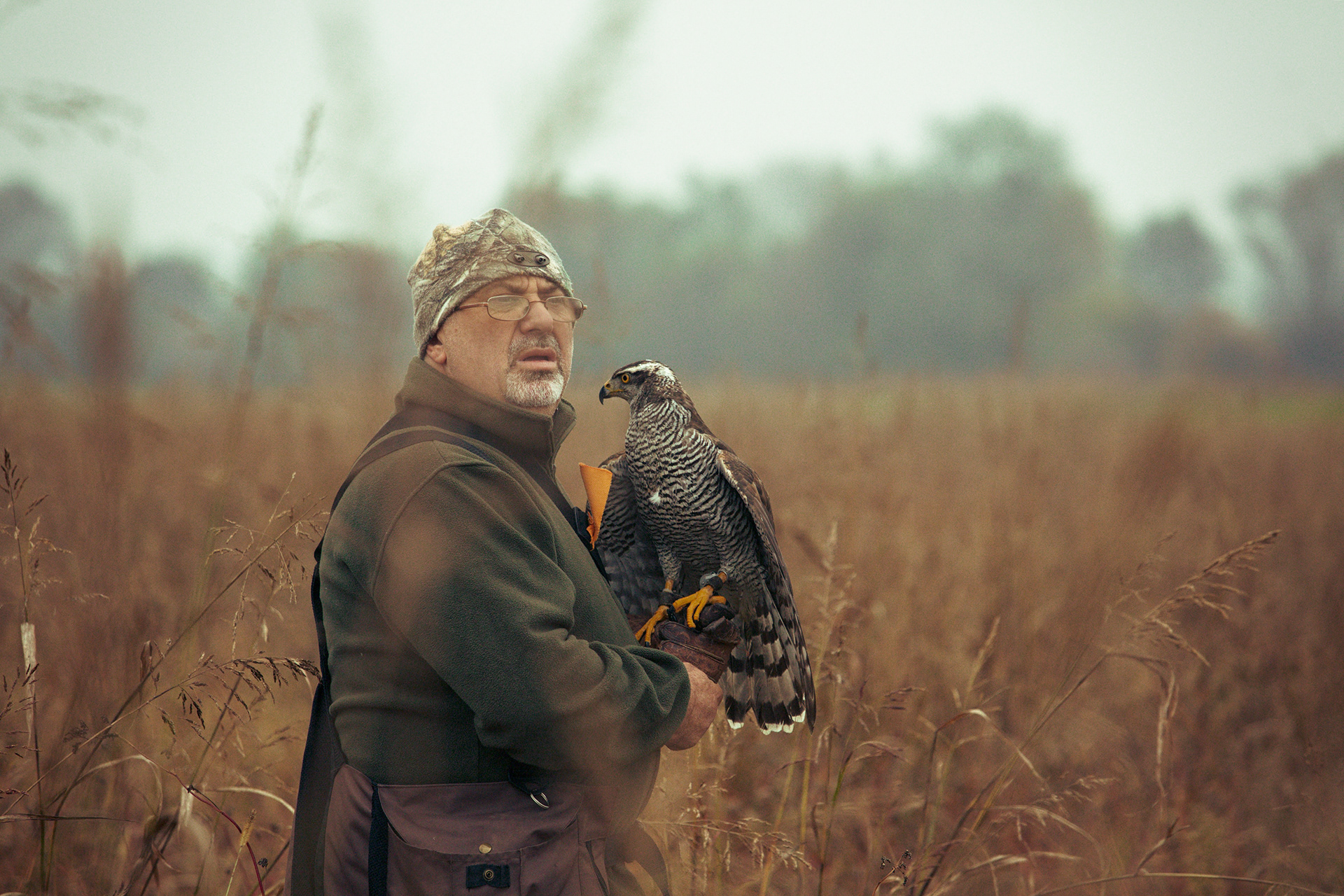
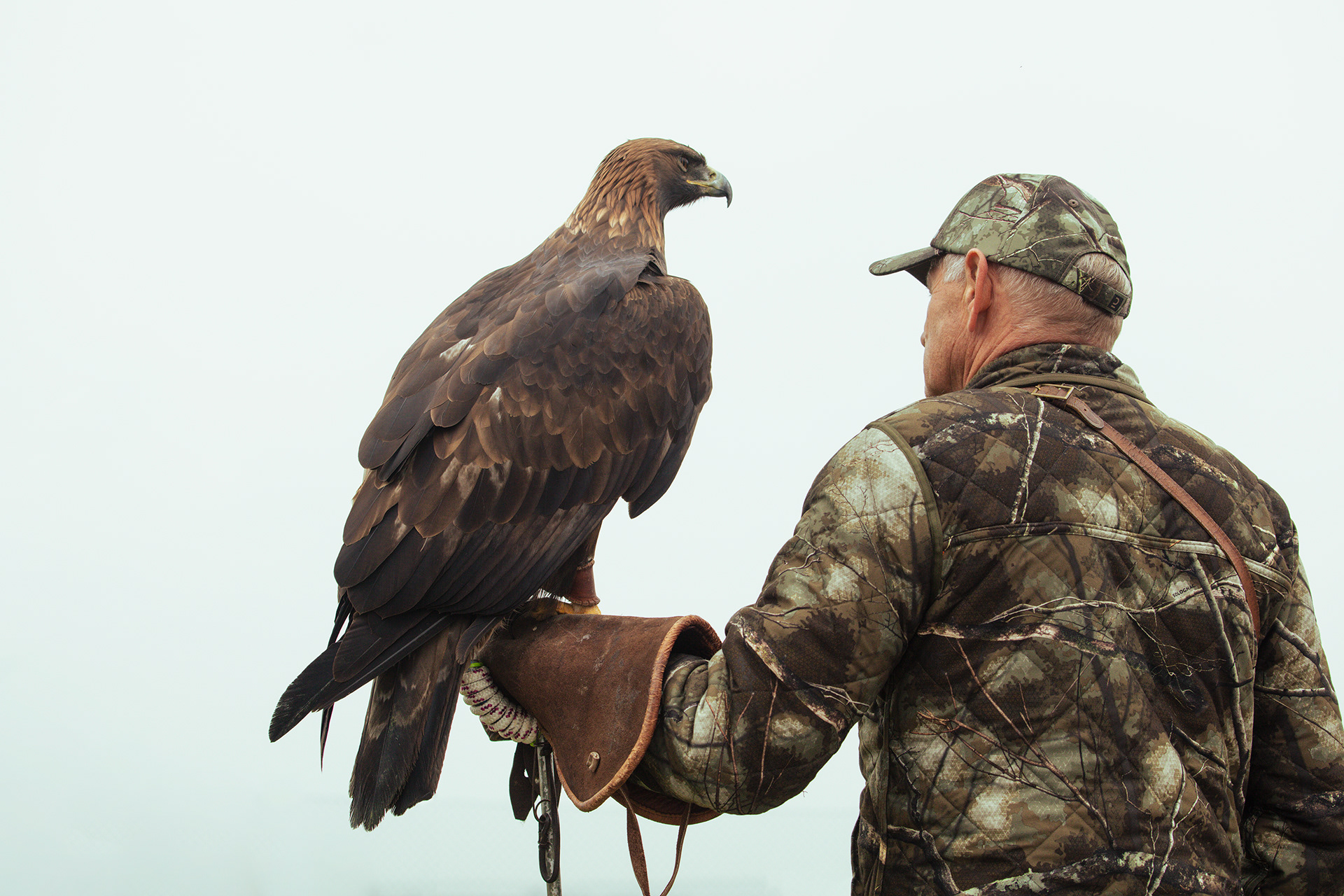
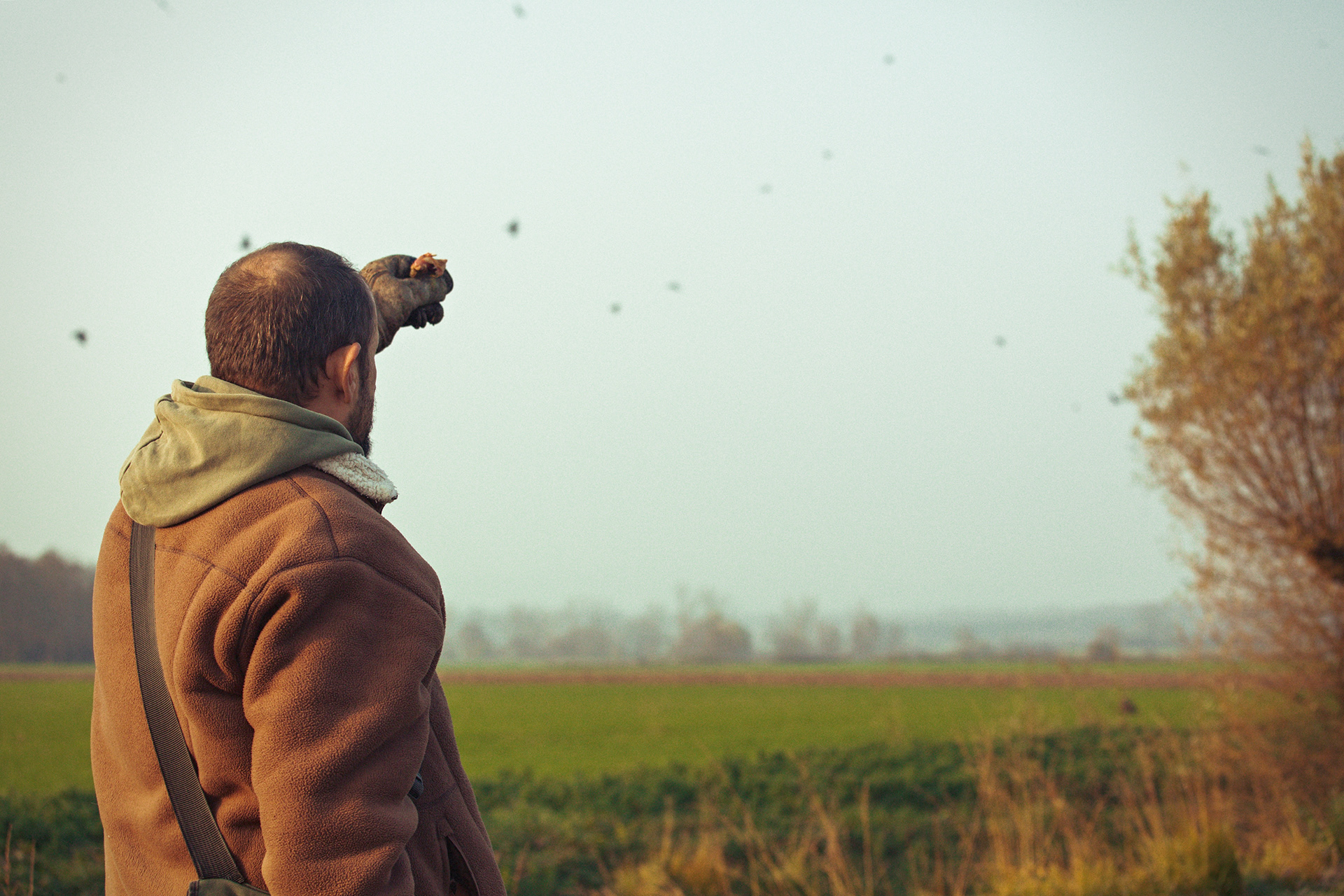
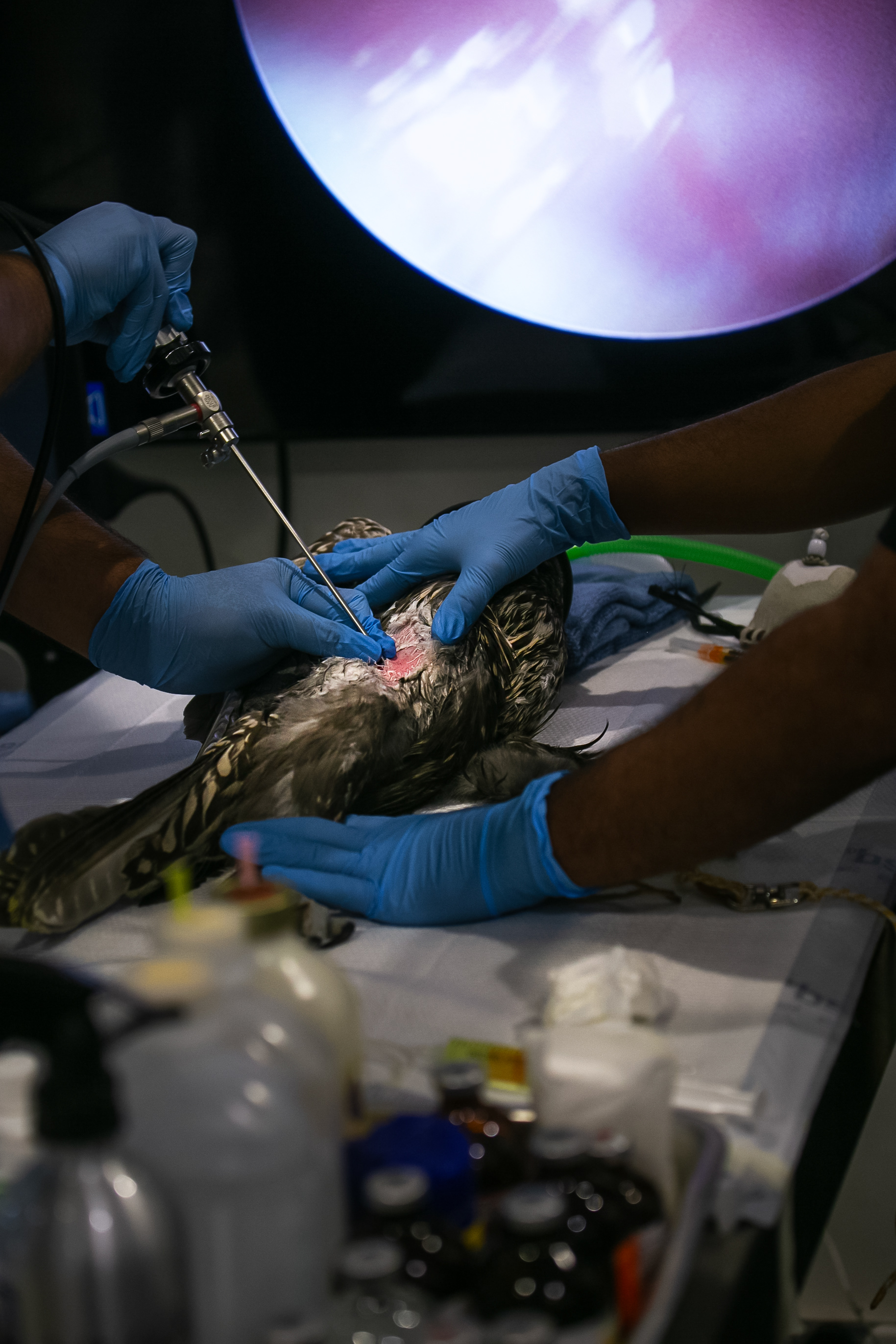
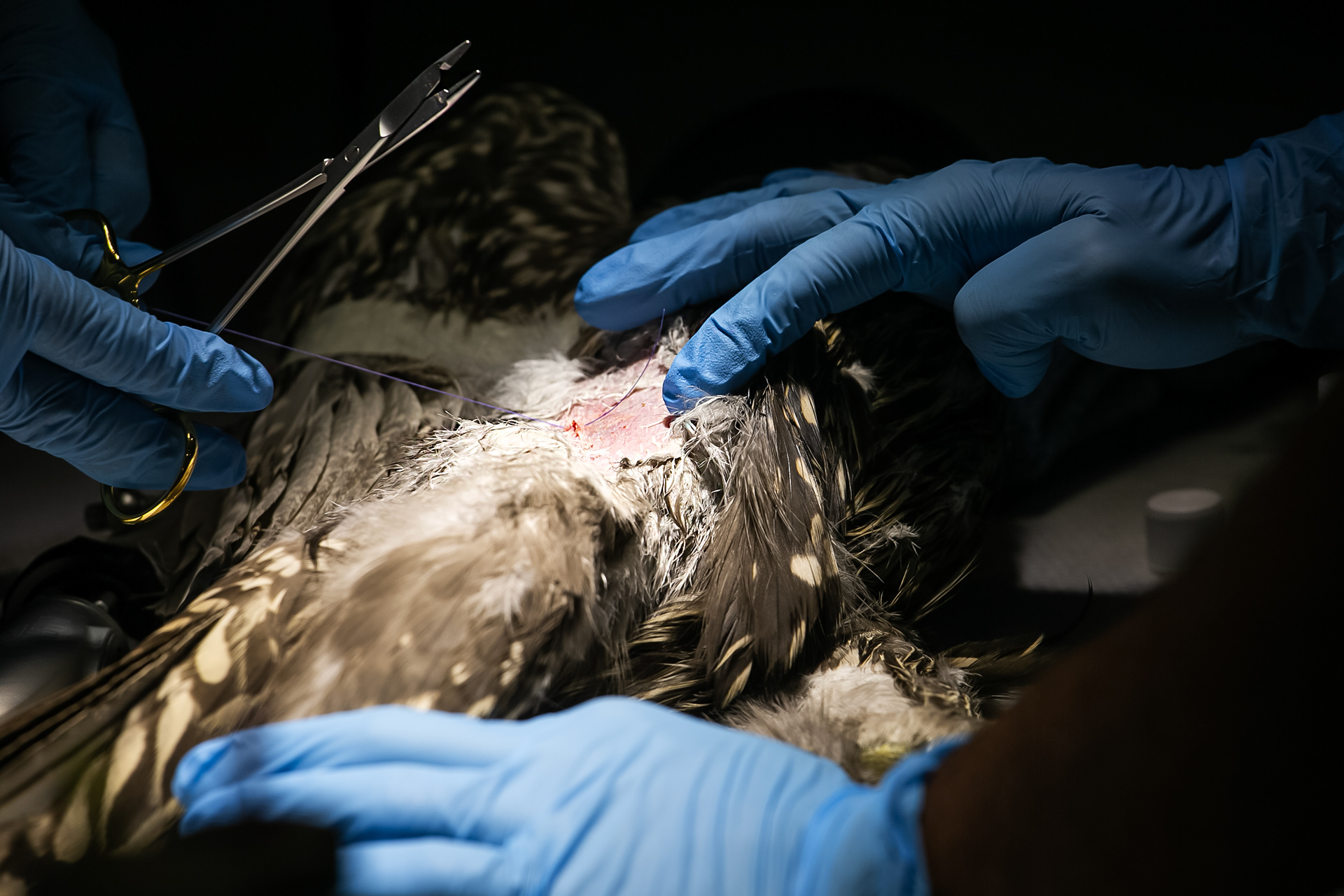
FALCONRY
In an age where technology permeates every aspect of life, some still look to the sky in search of a genuine connection with nature. Falconry – the ancient art of hunting with birds of prey – remains one of the noblest forms of human coexistence with the wild.
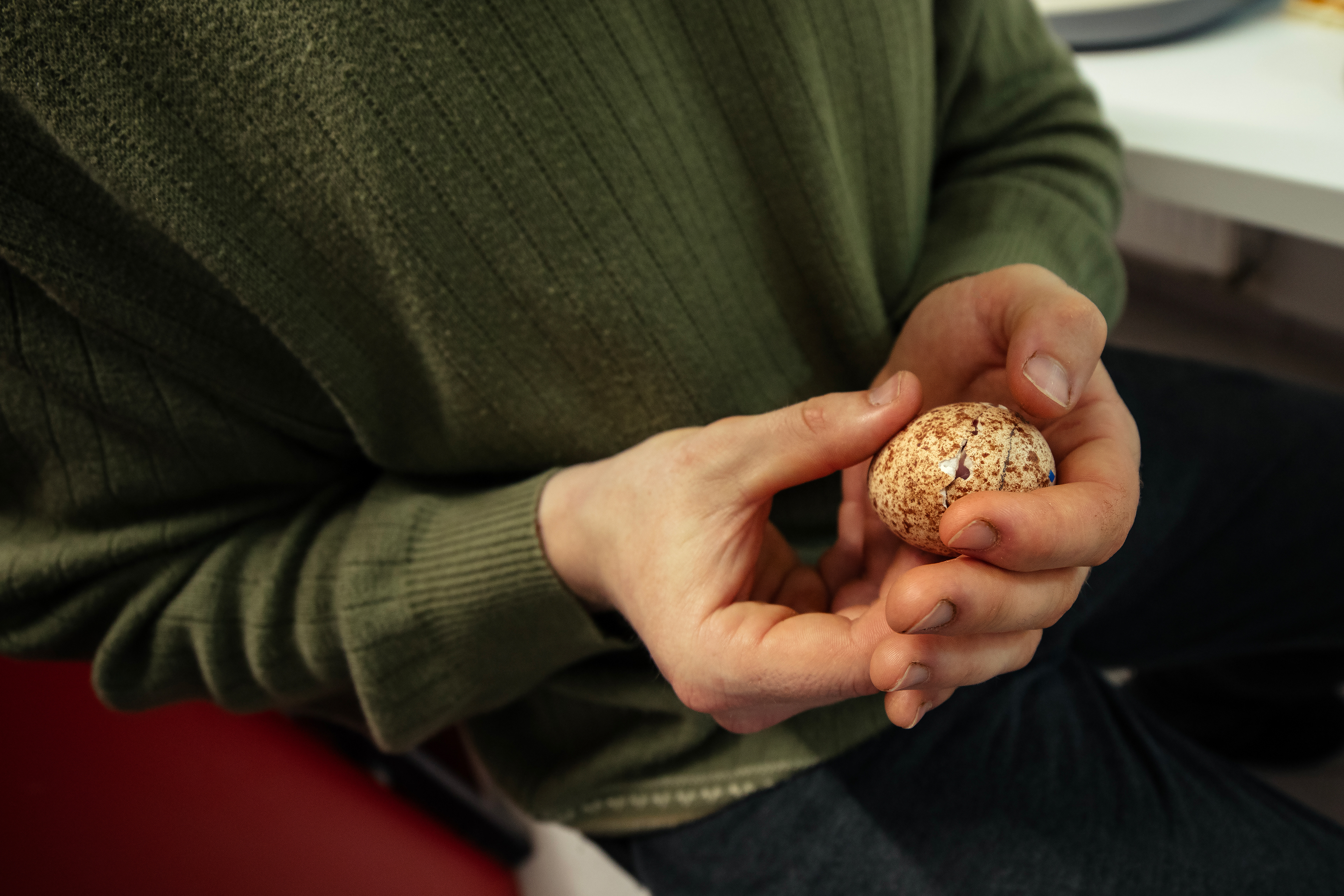
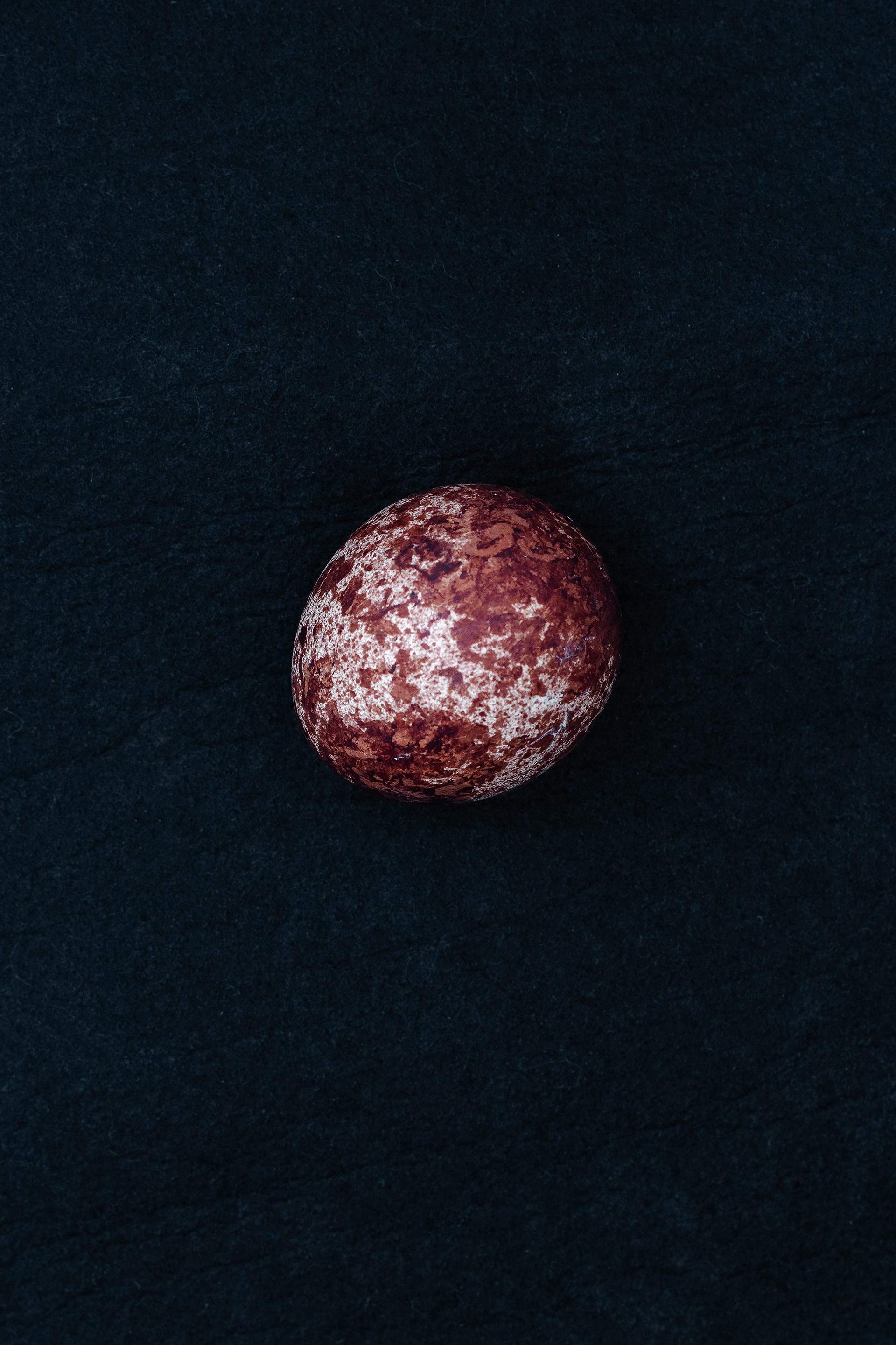
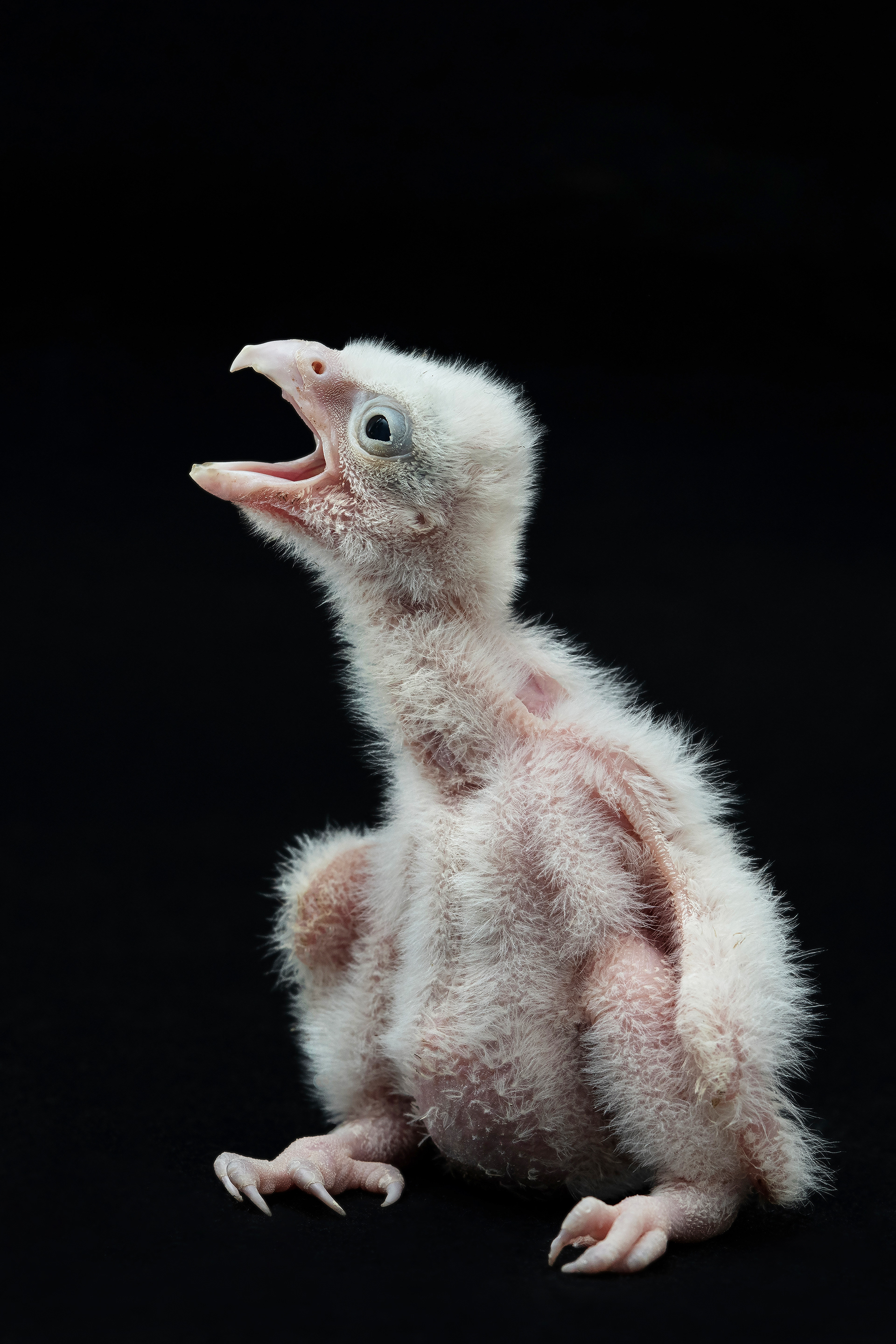
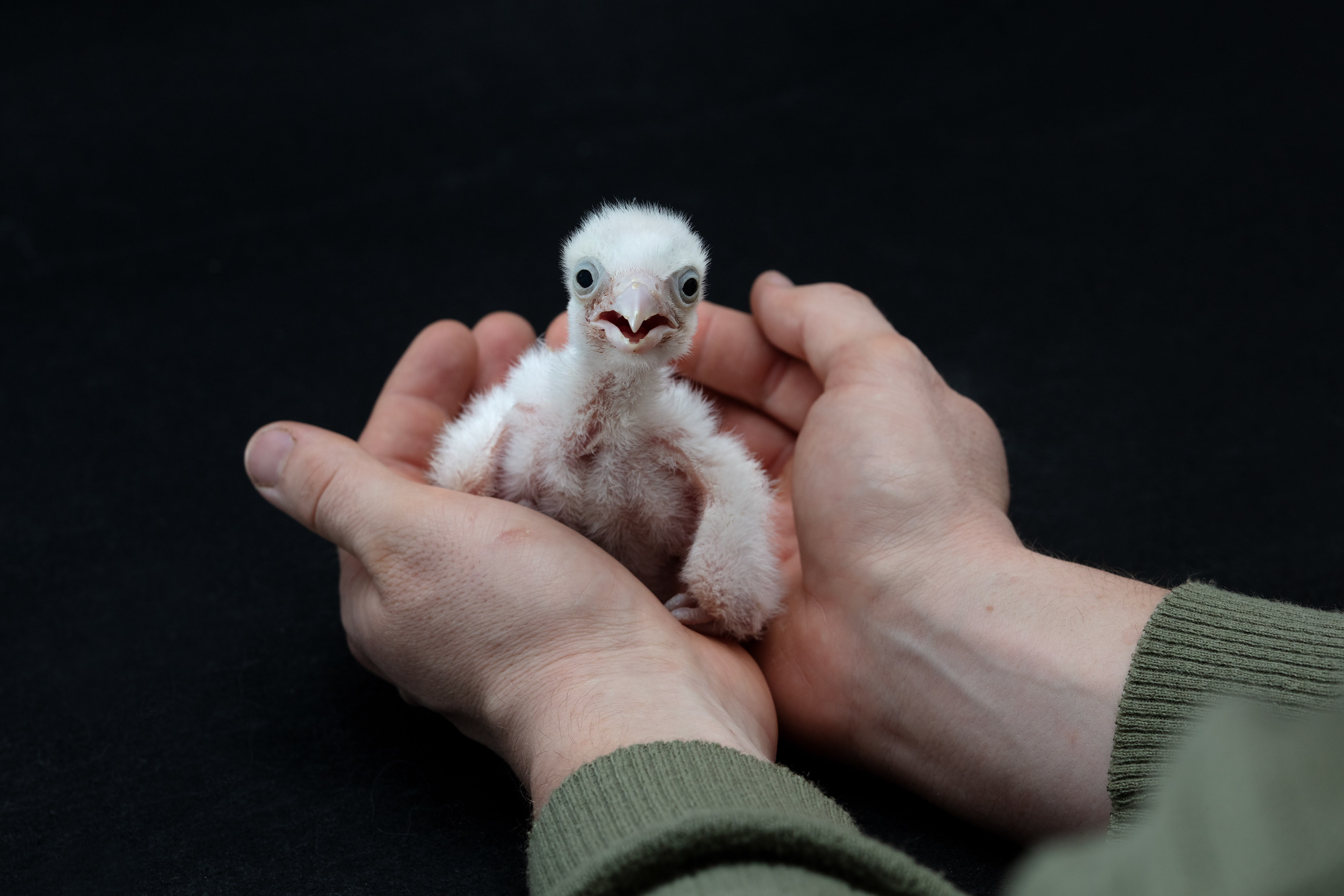
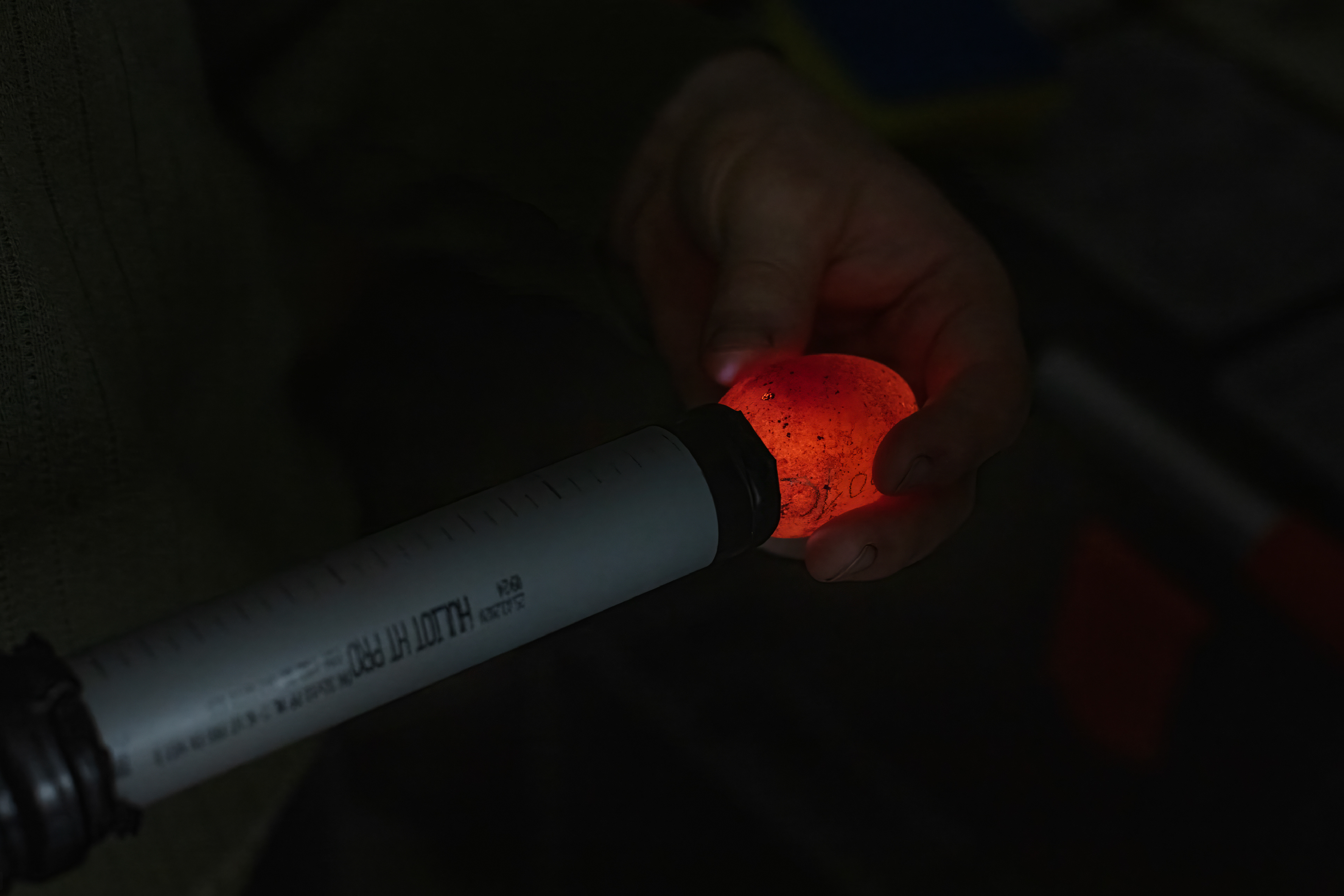
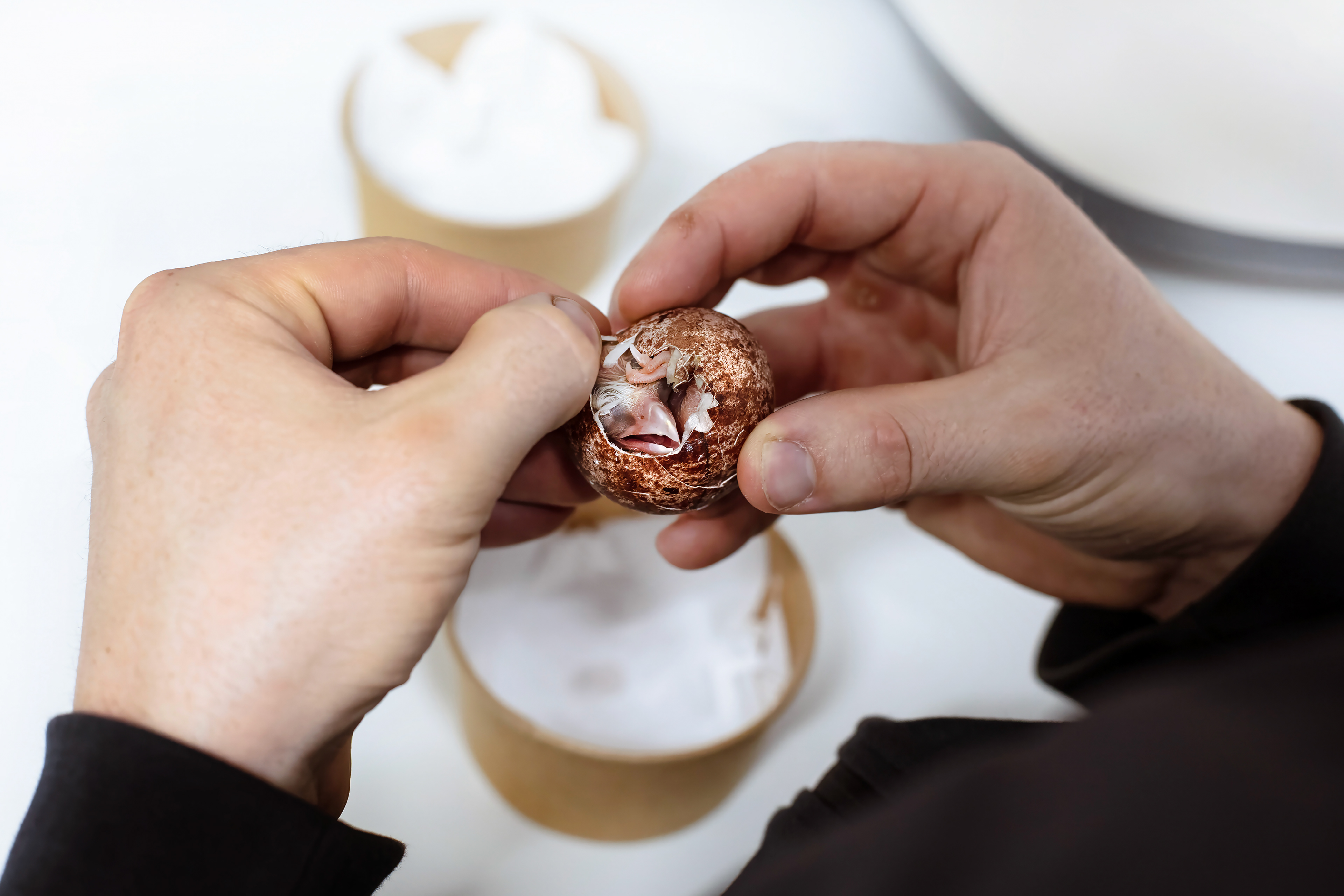
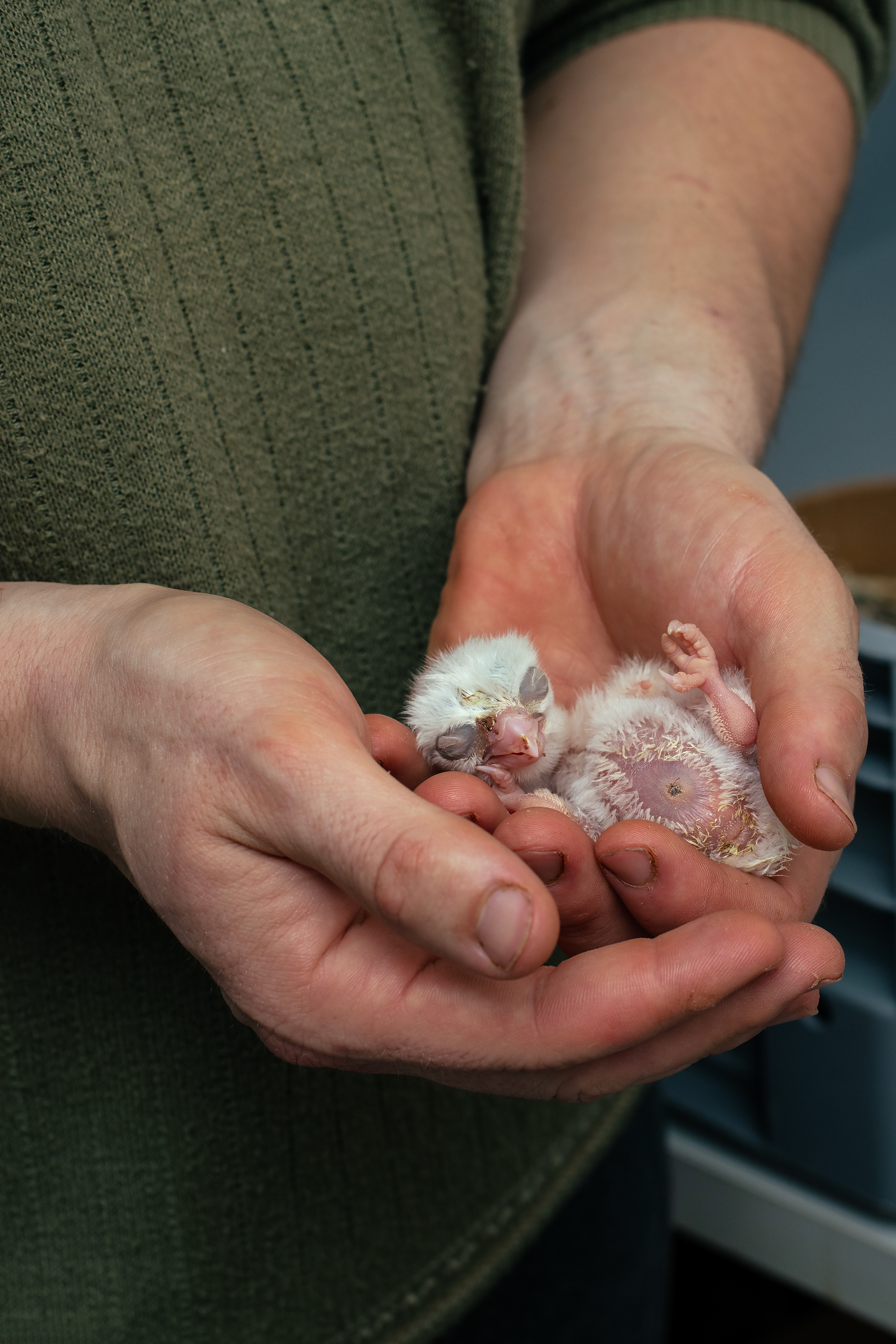
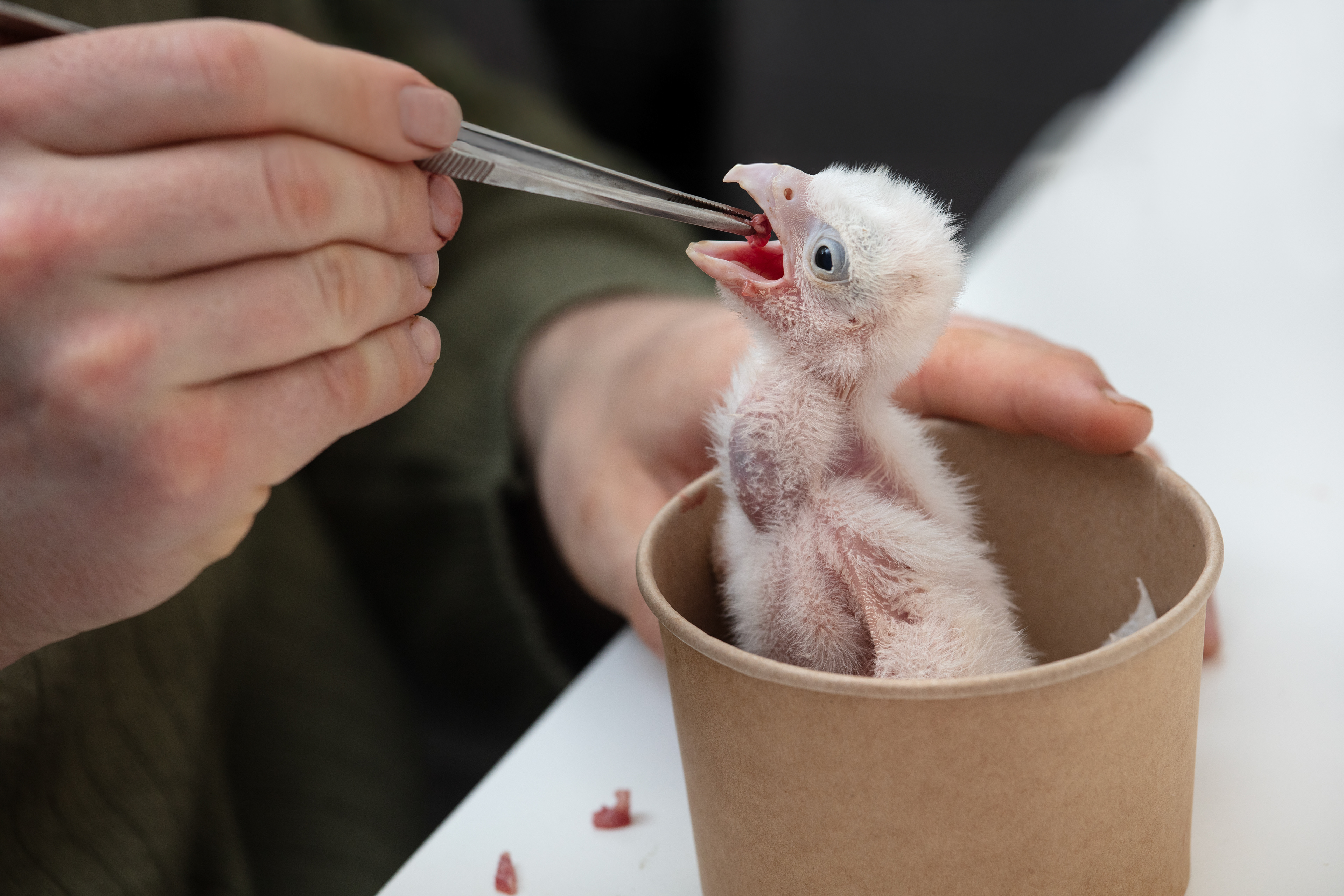
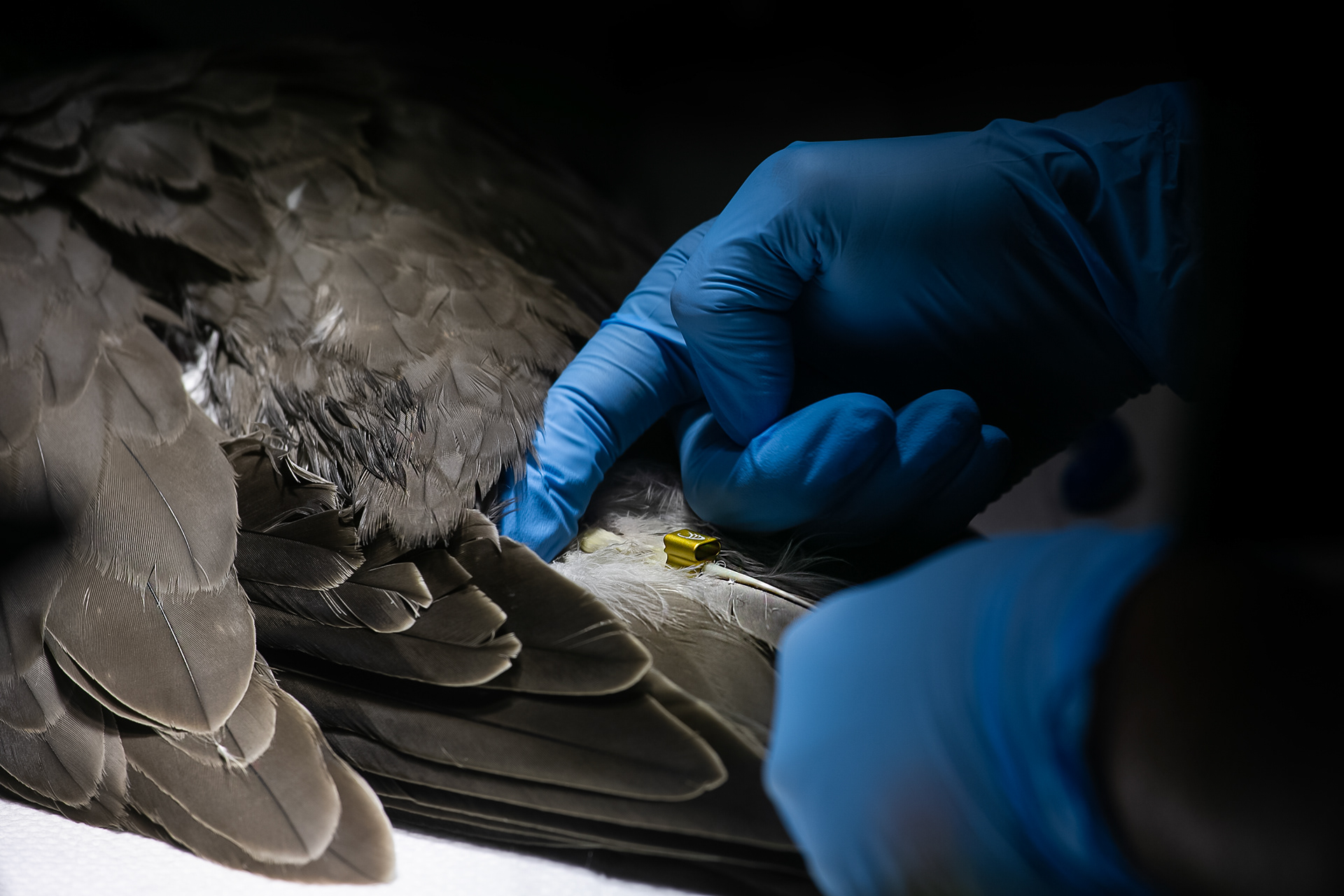
Today, however, falconry is no longer just the art of hunting. It has become a fight for survival, literally – for every single egg that can mean the continuation of an endangered species.
At a time when nature is retreating from man, every hatched bird is a symbol of resistance against oblivion. And every falconer who cares for that bird is its silent guardian.
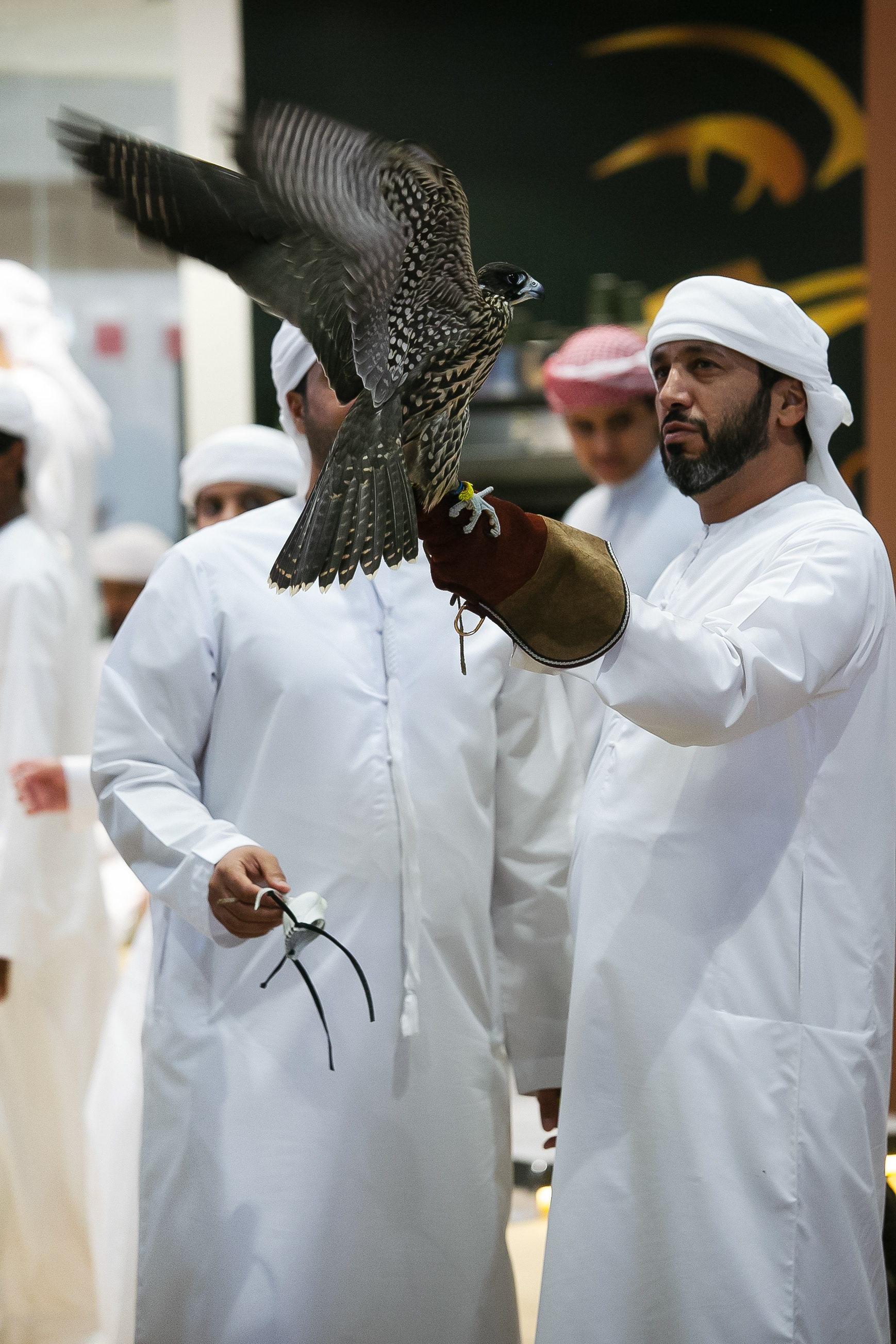
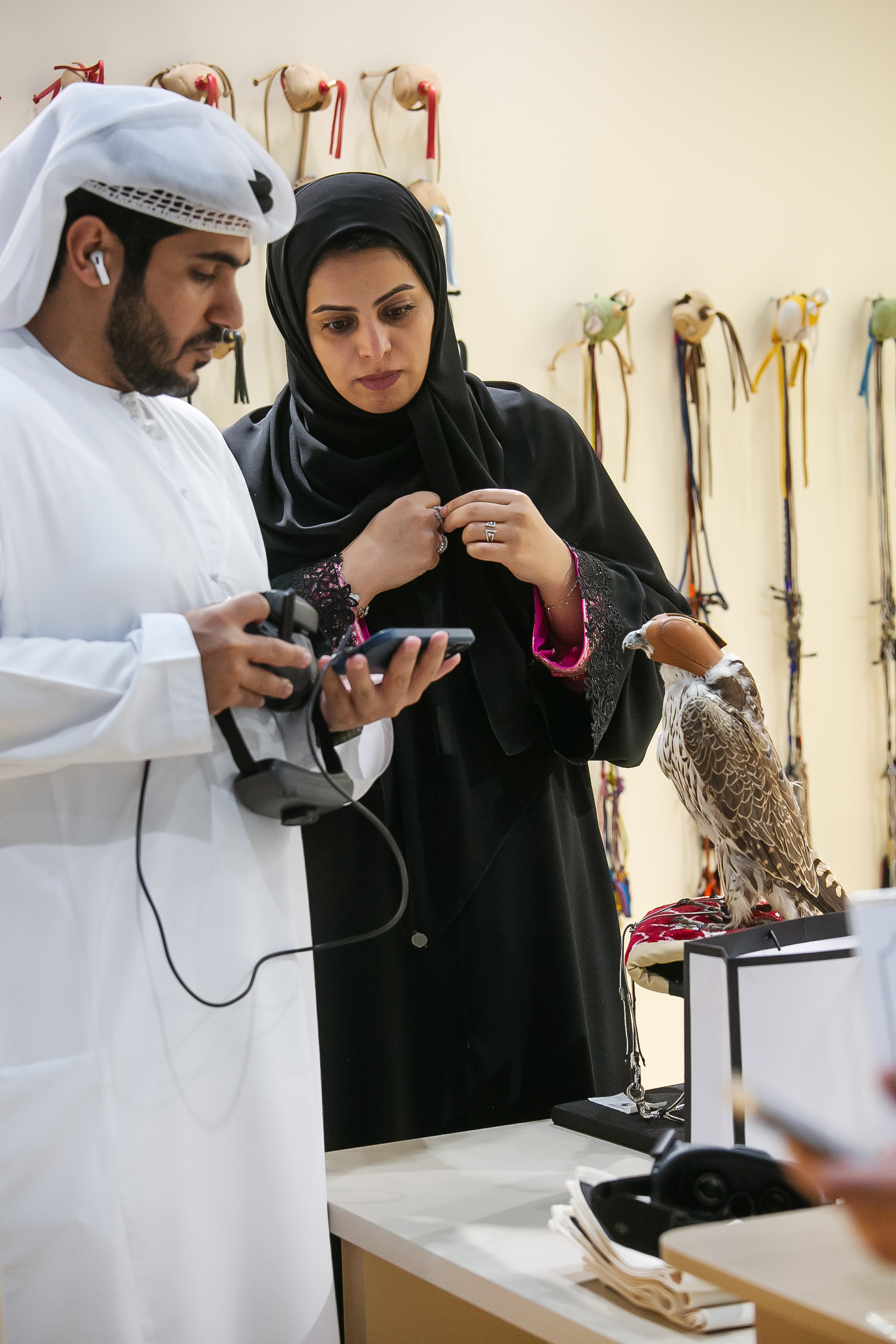
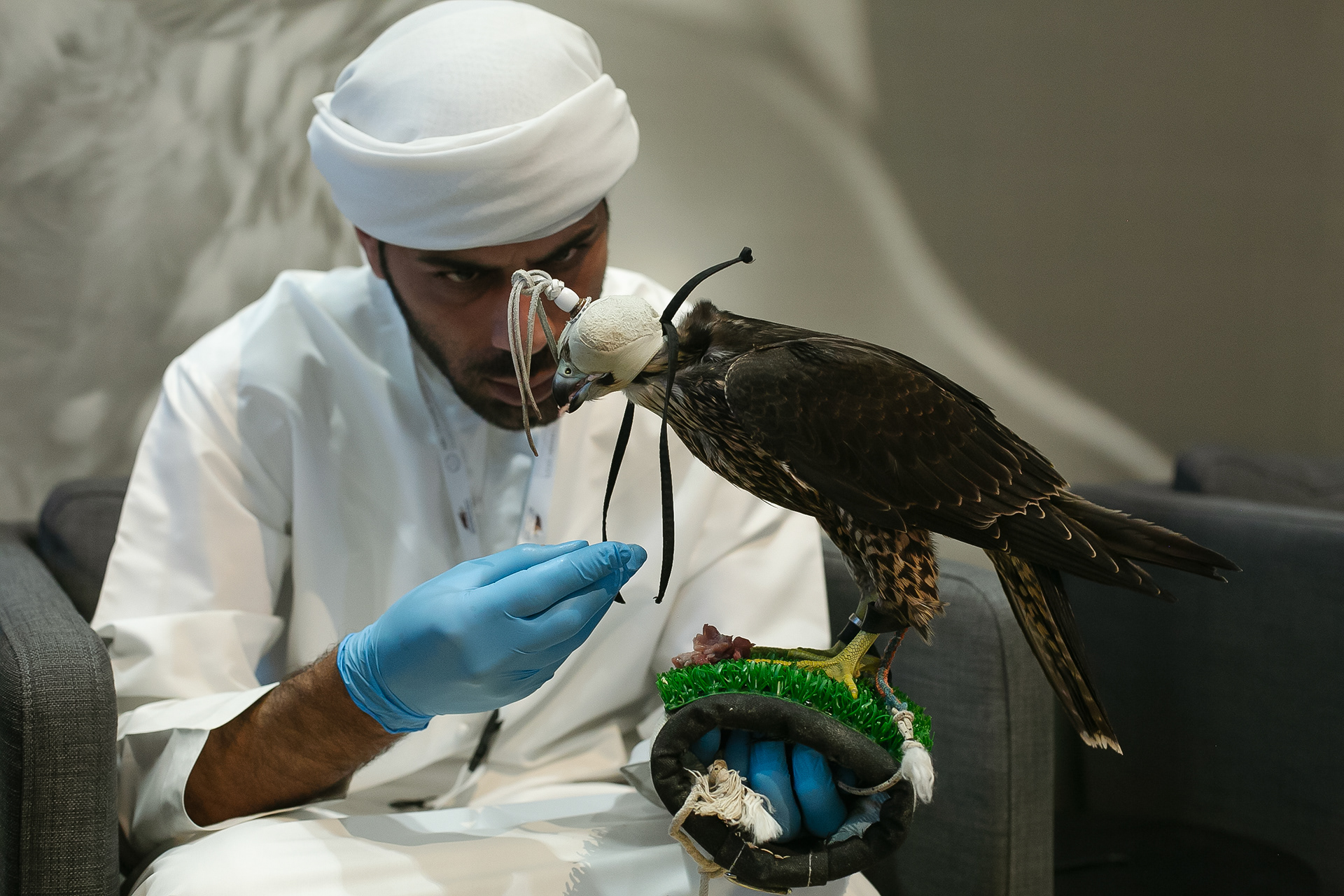
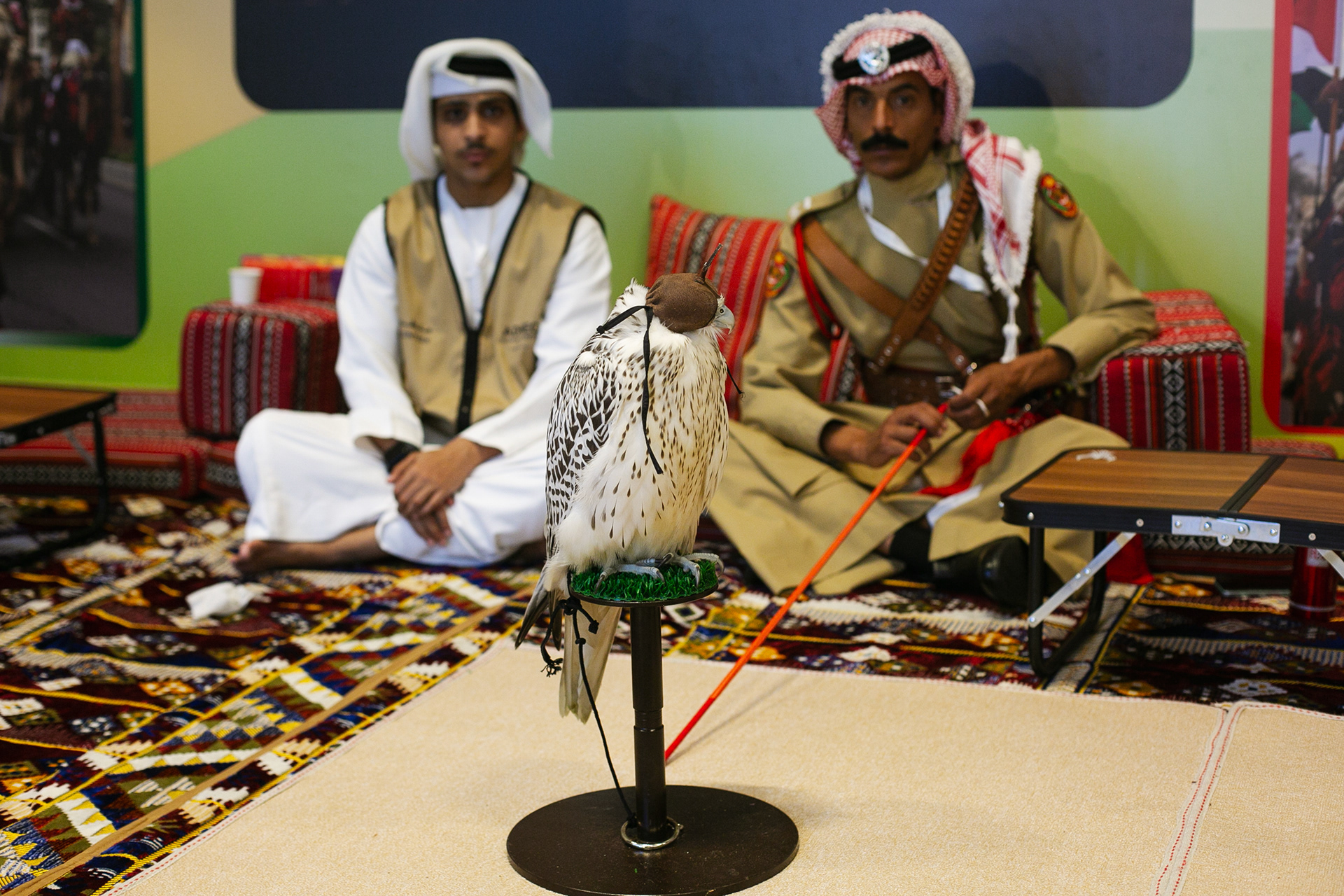
Falcon is not just a bird. It is a partnership. It is an ally. And often – the last link with nature that a person can still understand with body and soul.
In Slovenija is a centuries-old tradition that blends skill, respect for nature, and a deep bond between falconers and their birds of prey. Recognized by UNESCO as an Intangible Cultural Heritage, Slovenian falconers uphold this ancient art with dedication, training falcons for hunting and nature conservation.

























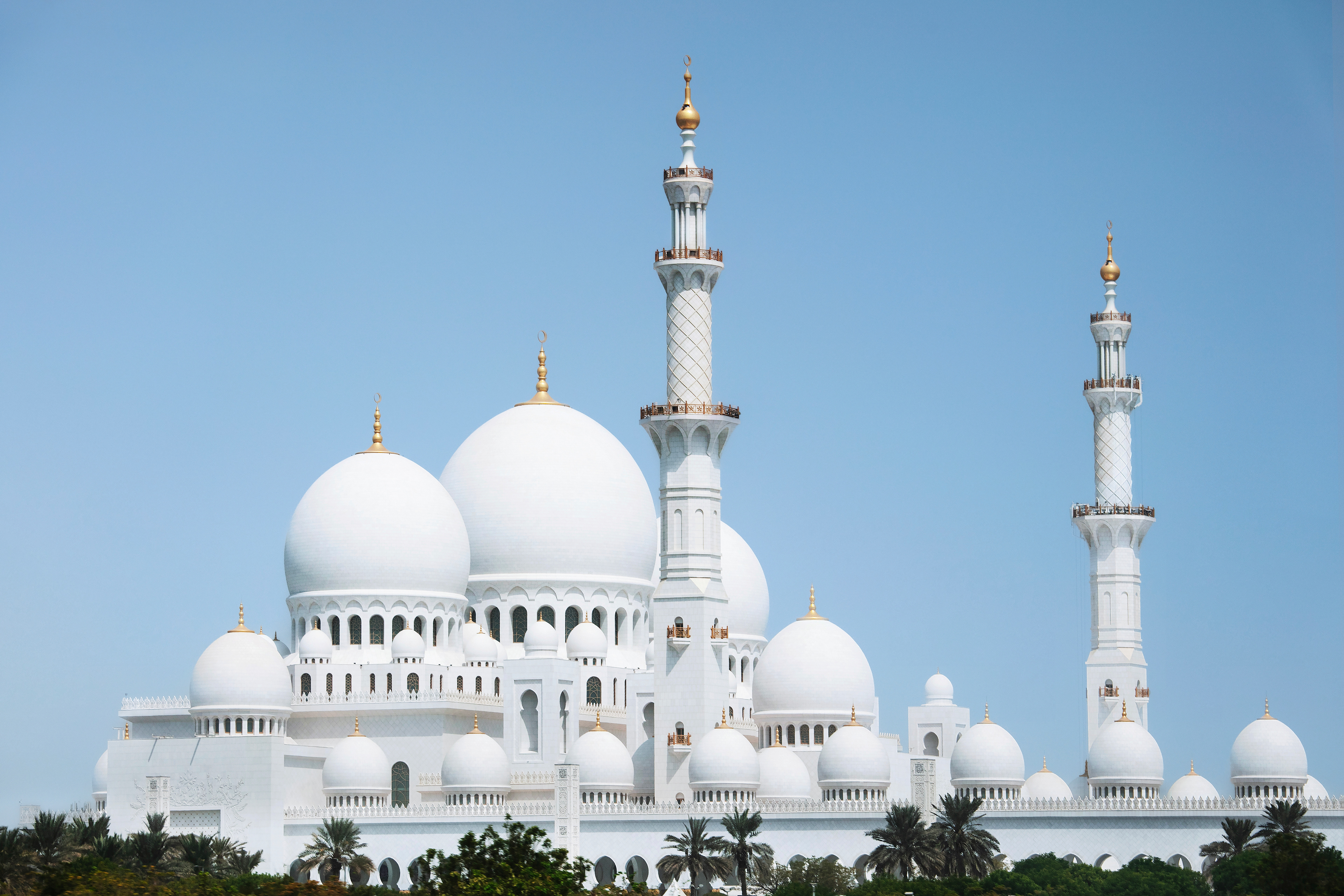
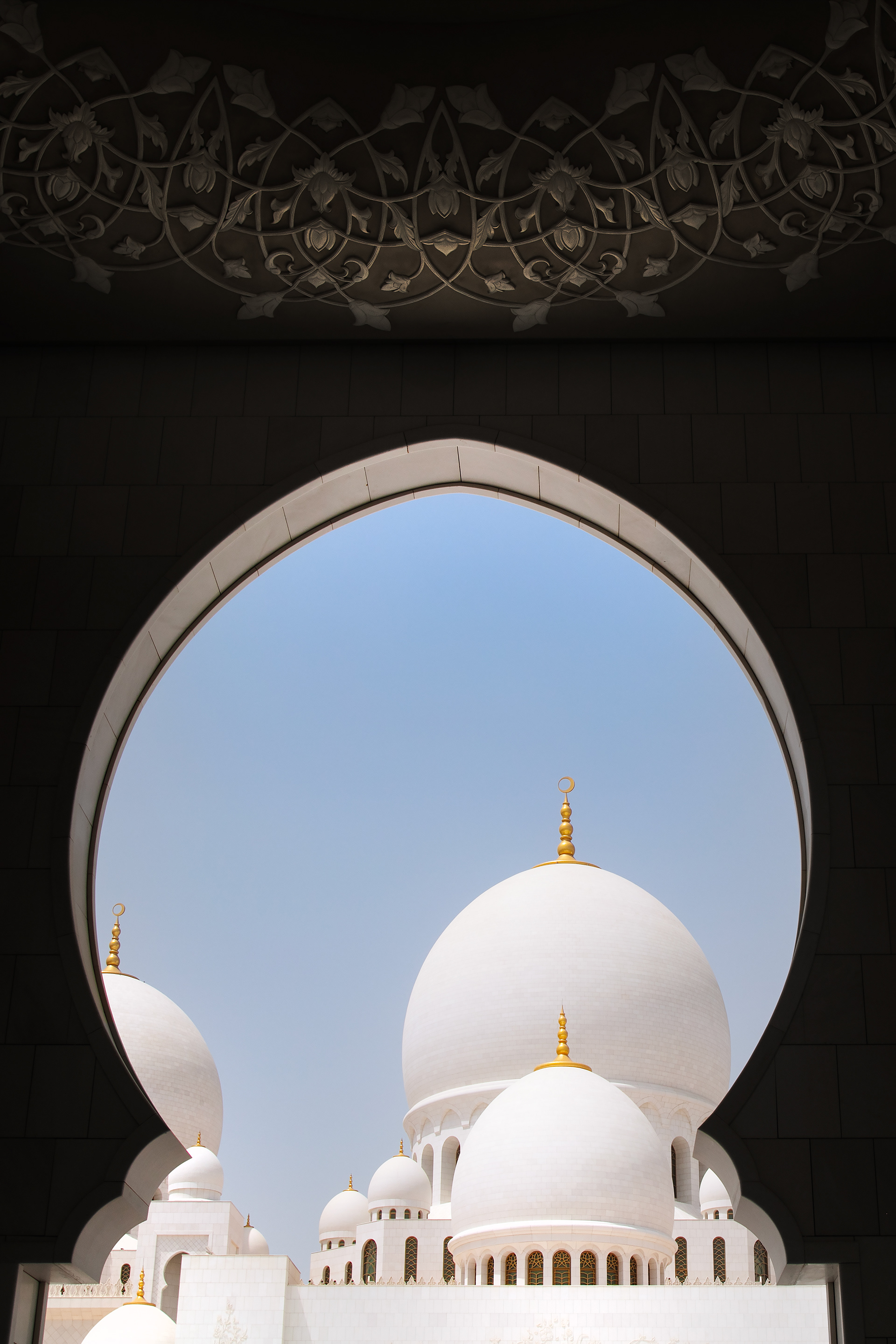
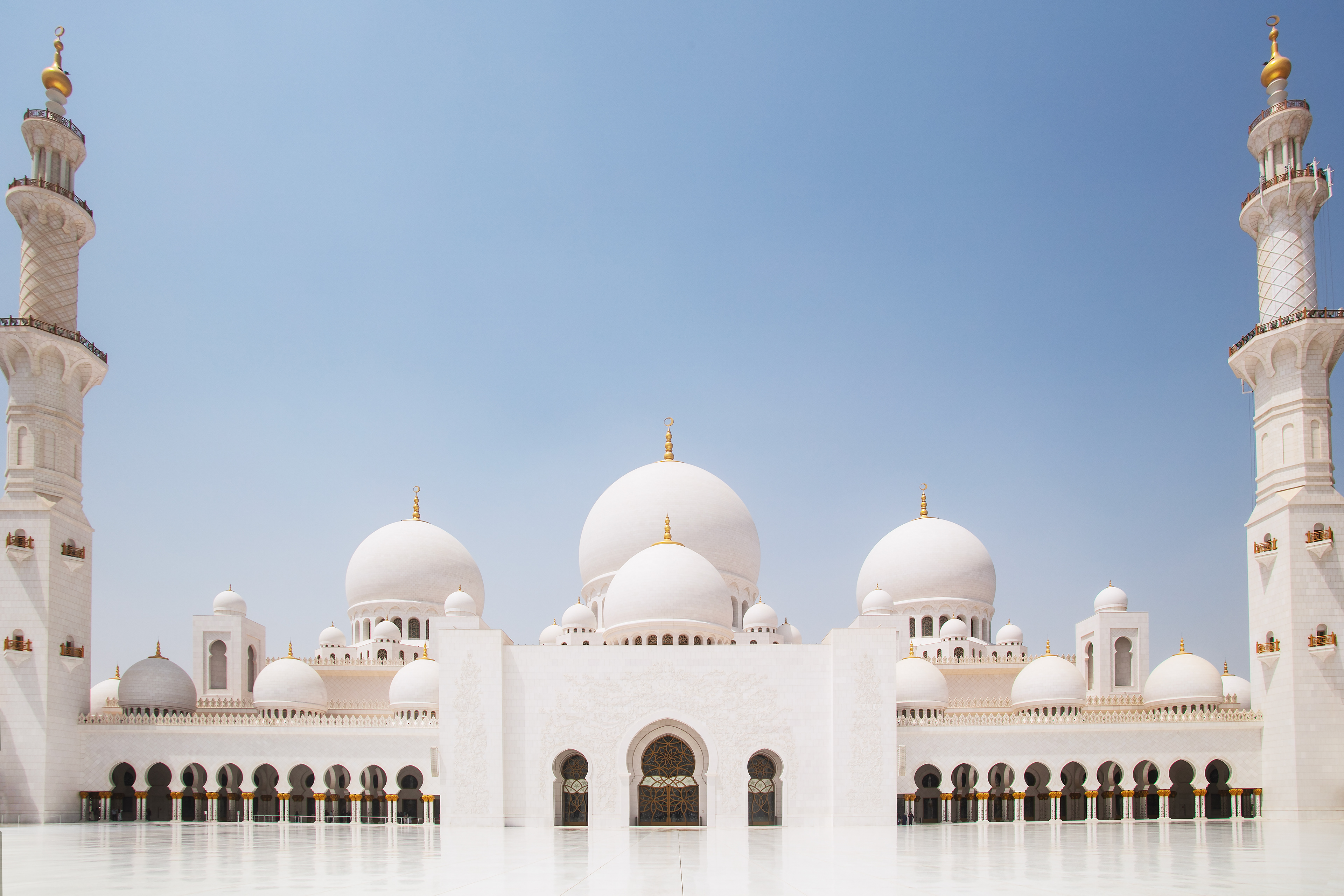
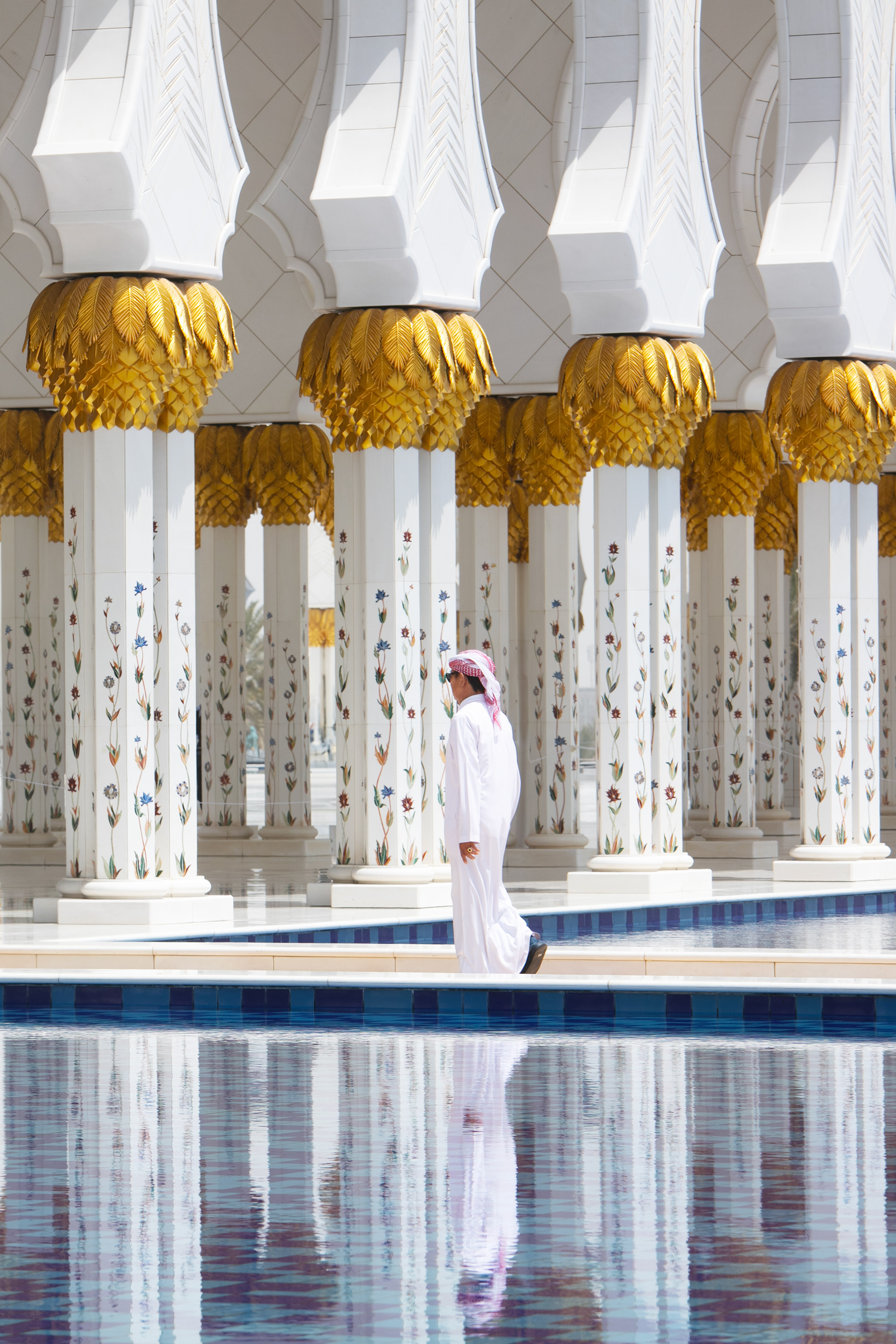
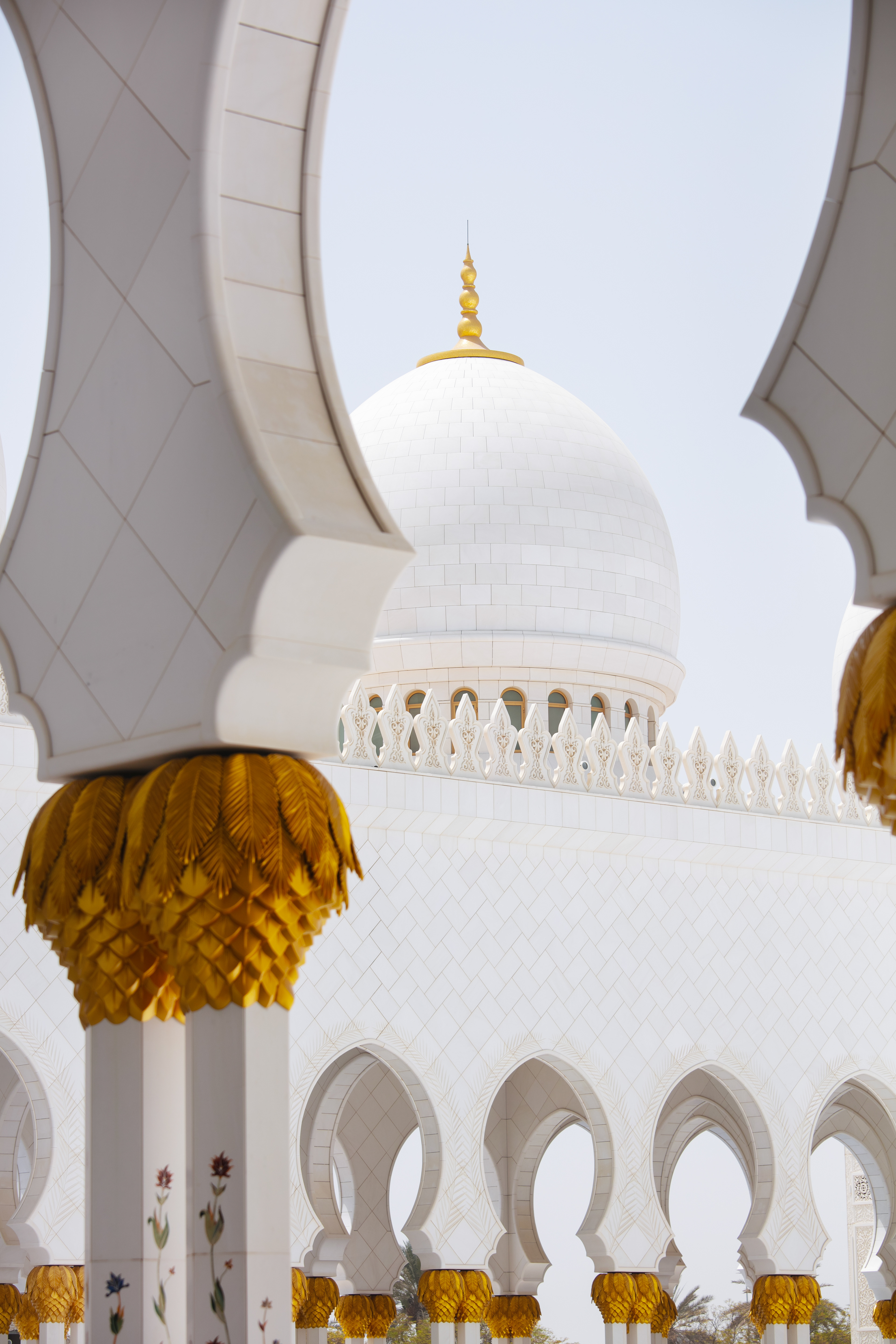
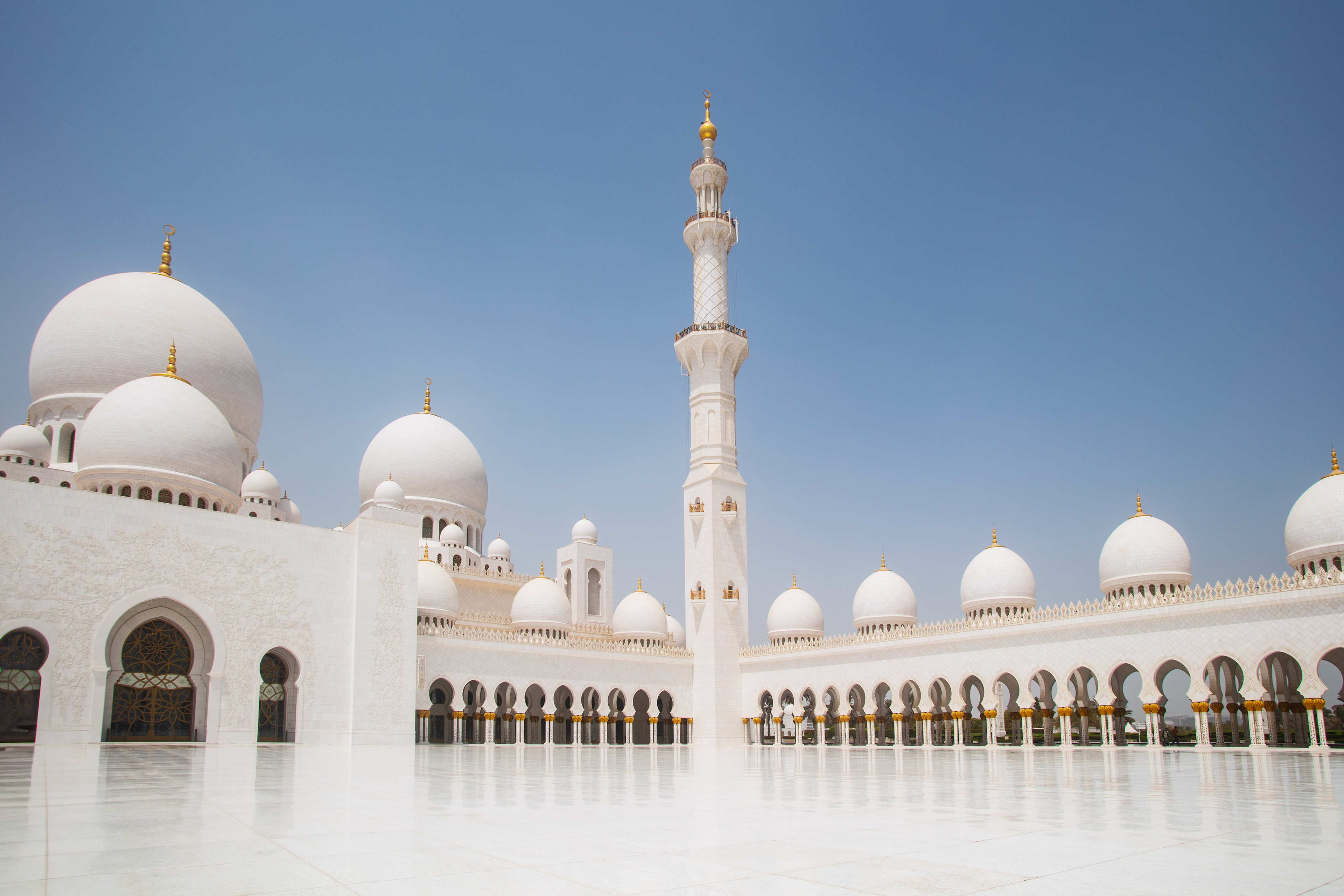
THE SHEIKH ZAYED GRAND MOSQUE
in Abu Dhabi City is not only one of the world’s largest mosques. It’s a place where tradition meets breathtaking beauty. The dazzling white marble, endless reflections, and peaceful silence make it one of the most magical places I’ve ever visited.
With 82 shining domes, more than 1,000 columns, and one of the world’s largest chandeliers, the mosque is really an architectural wonder.
Inside the prayer hall is another treasure: the largest hand-knotted carpet on Earth, covering around 5,600 m². It was crafted by more than 1,200 Iranian artisans and took nearly two and a half years to complete.
With over 2.2 billion knots and weighing more than 35 tons, this carpet is as extraordinary as the mosque itself. After being woven, it was carefully cut into pieces, transported to Abu Dhabi, and then reassembled inside the grand prayer hall – where it now adds to the mosque’s breathtaking atmosphere.










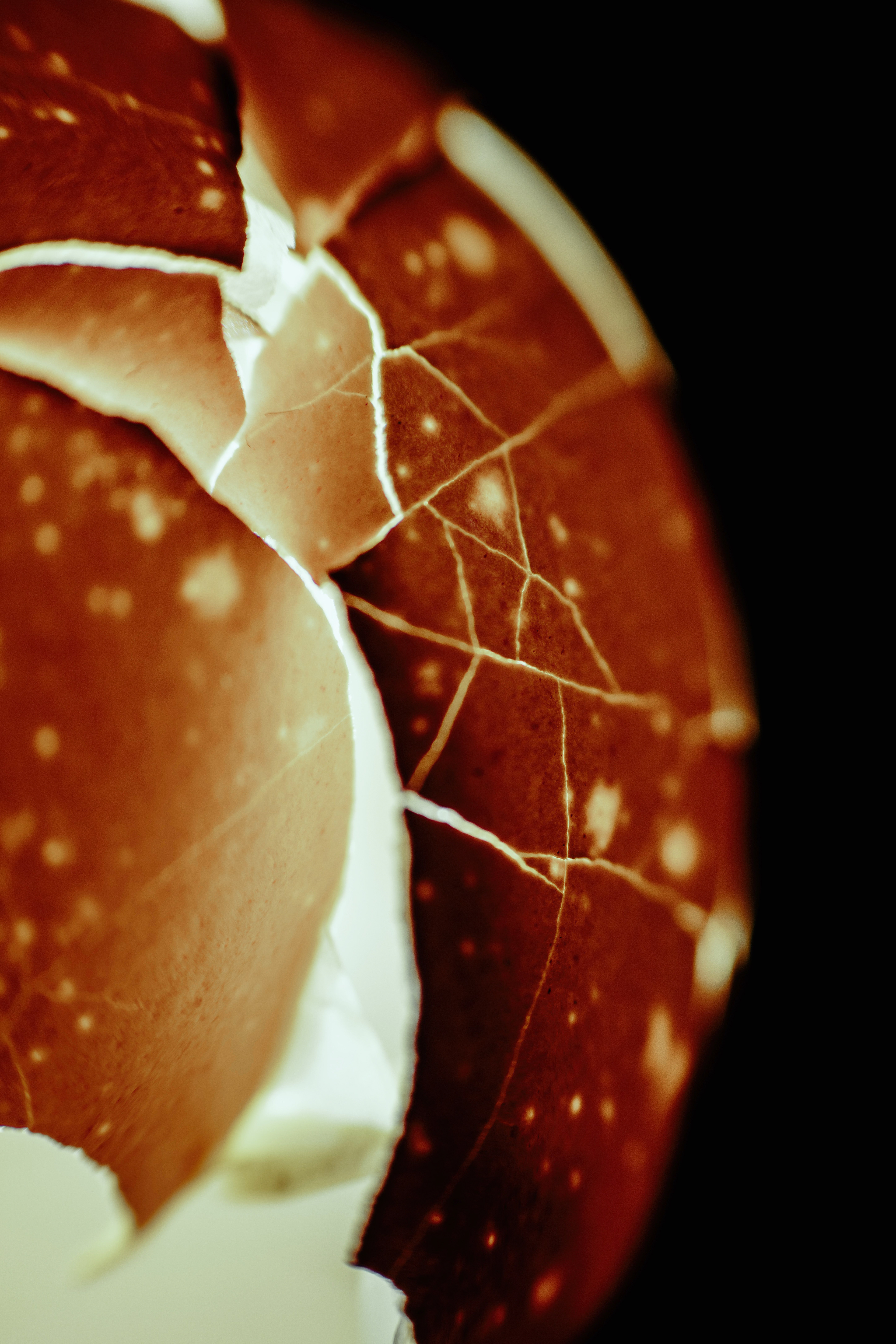
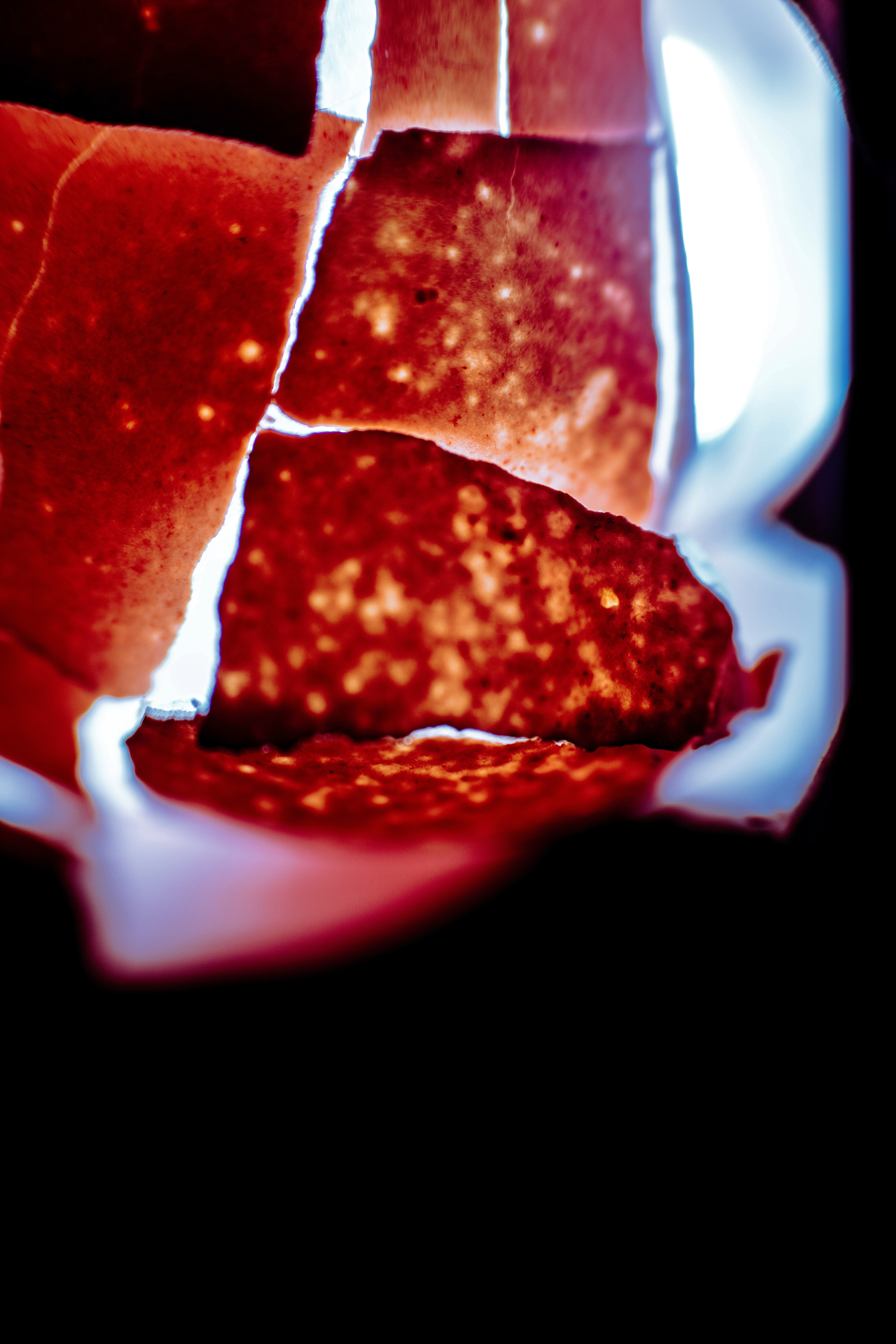
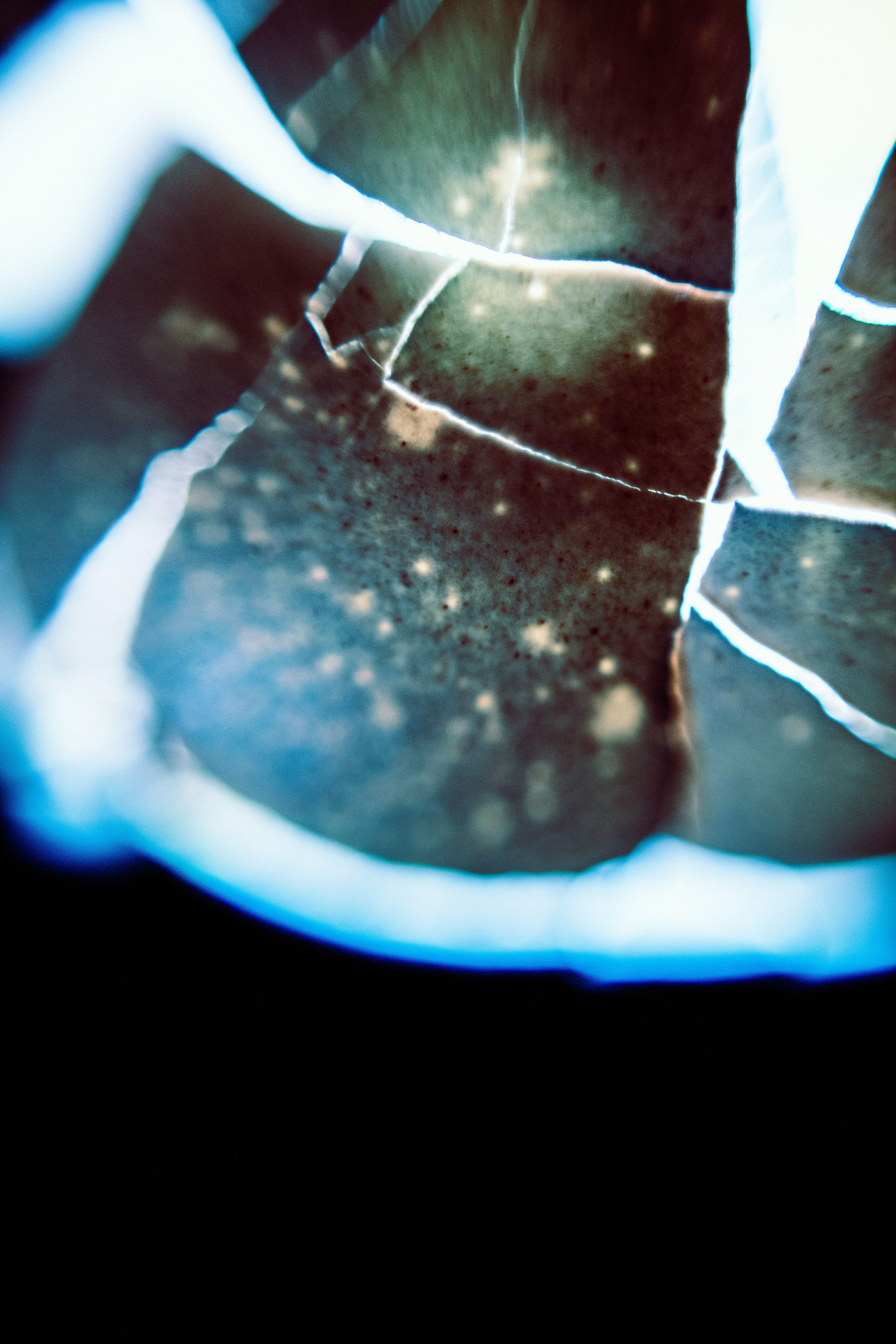
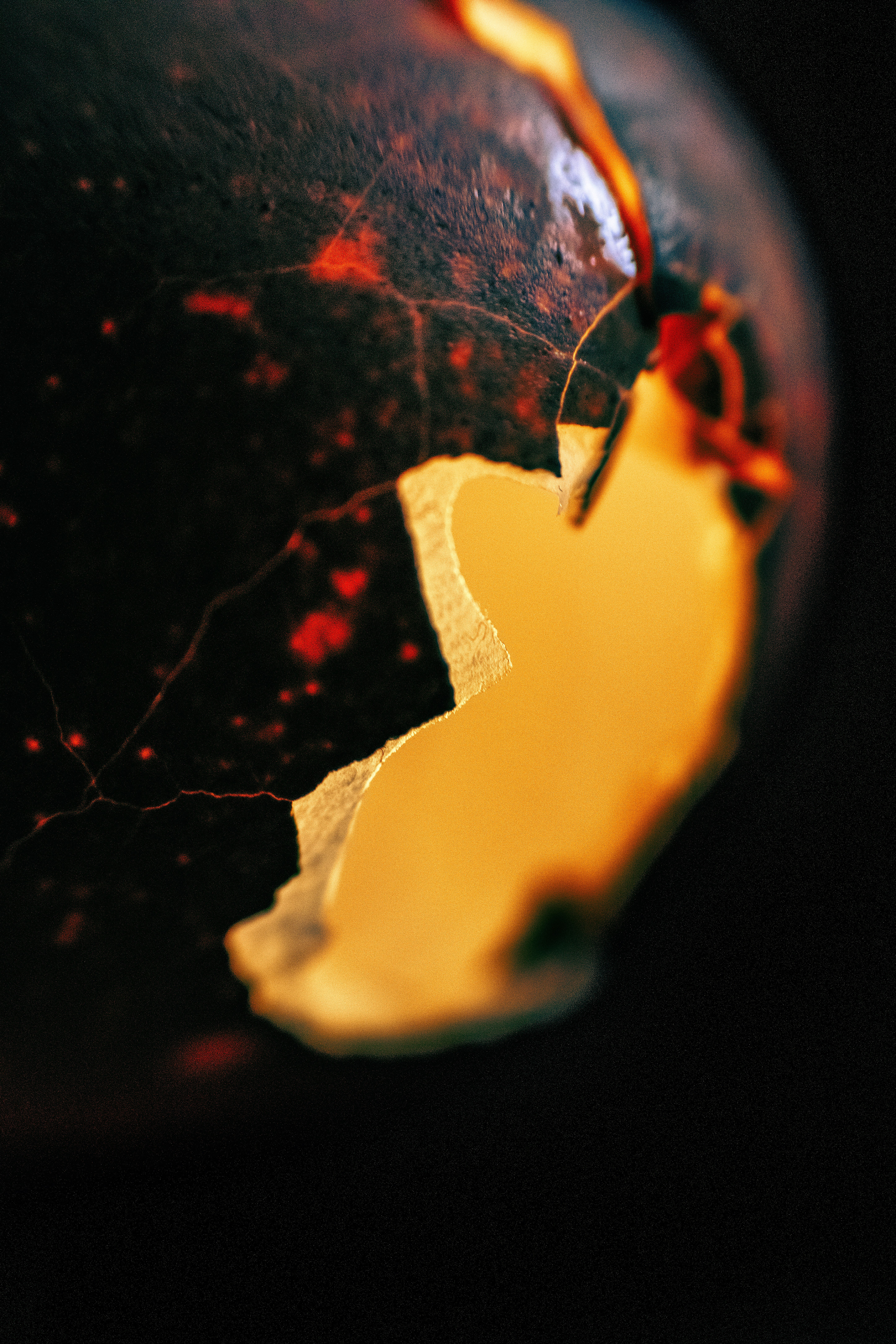
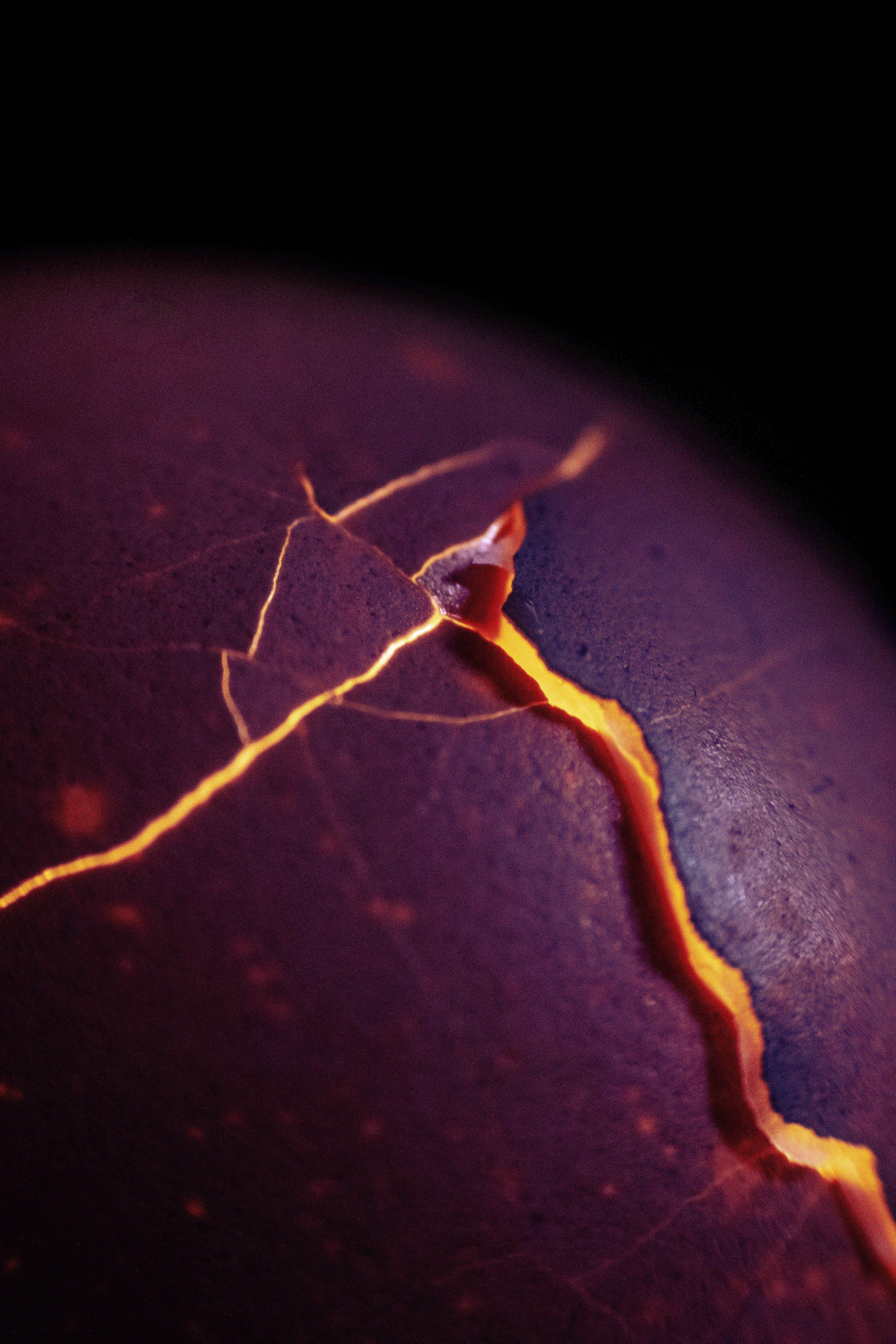
ART IS EVERYWHERE
— even in the simplest things. It is hidden in the everyday, waiting to be seen.
This images started as something simple — an egshell. But with the right light, focus, and perspective, it transformed into something entirely new—something abstract, mysterious, and almost otherworldly.
I love how photography allows me to find beauty in unexpected places. The delicate textures, the interplay of light and shadow, the way the colors shift — it all feels like a scene from a dream.
This is why I create. To remind myself, and hopefully others, that even the most ordinary things can hold magic if we take the time to see them differently.
And what do you see in this images?




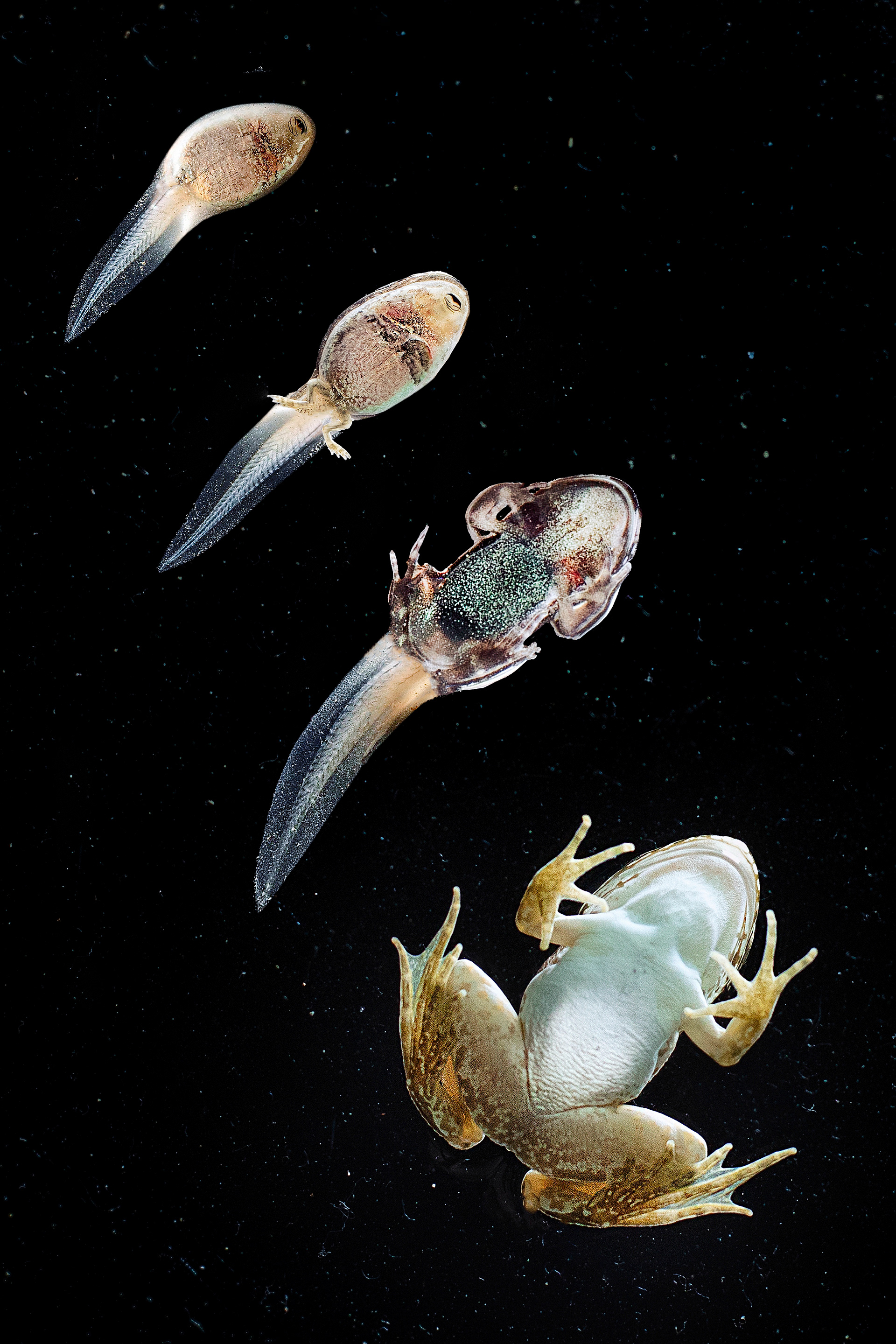
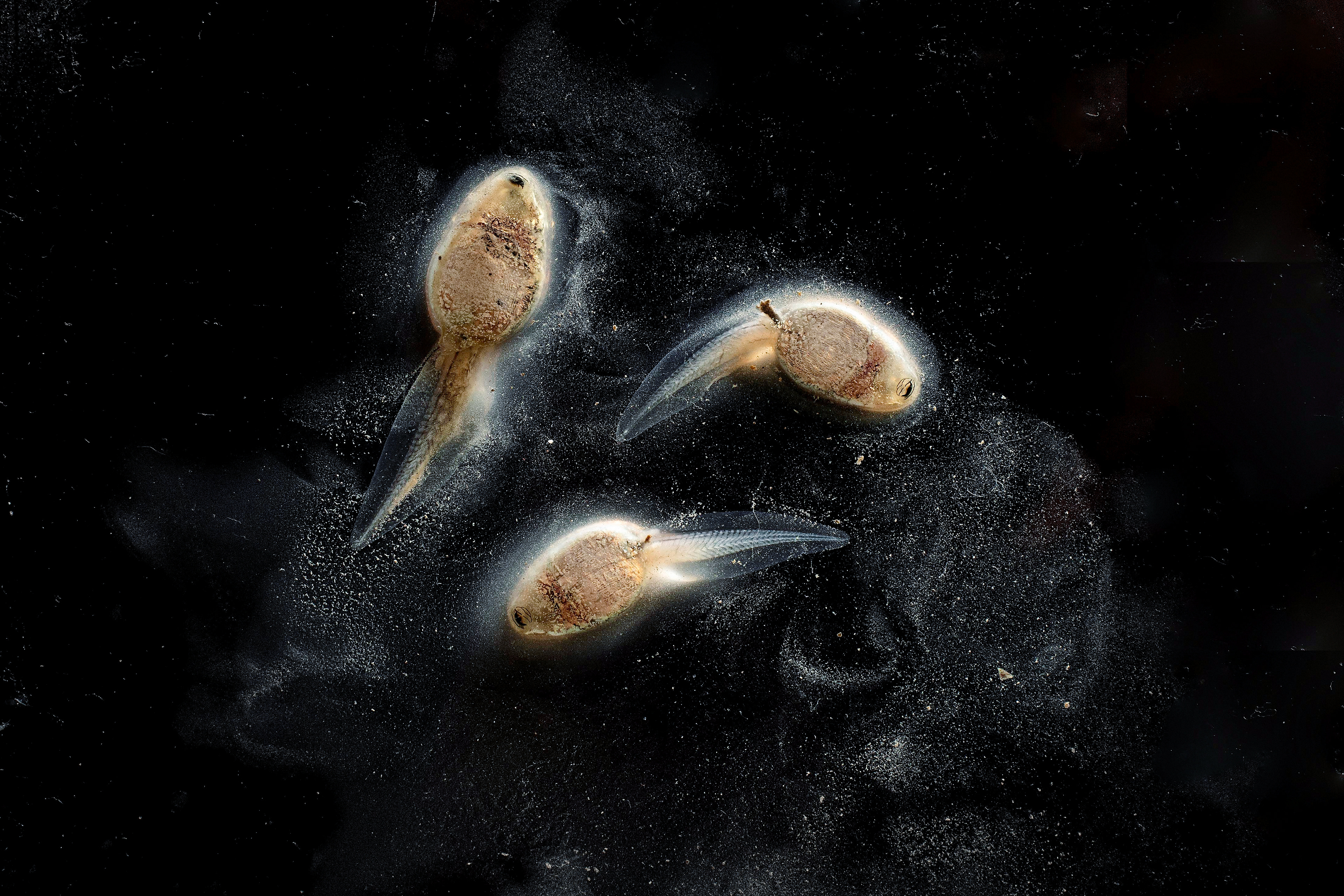
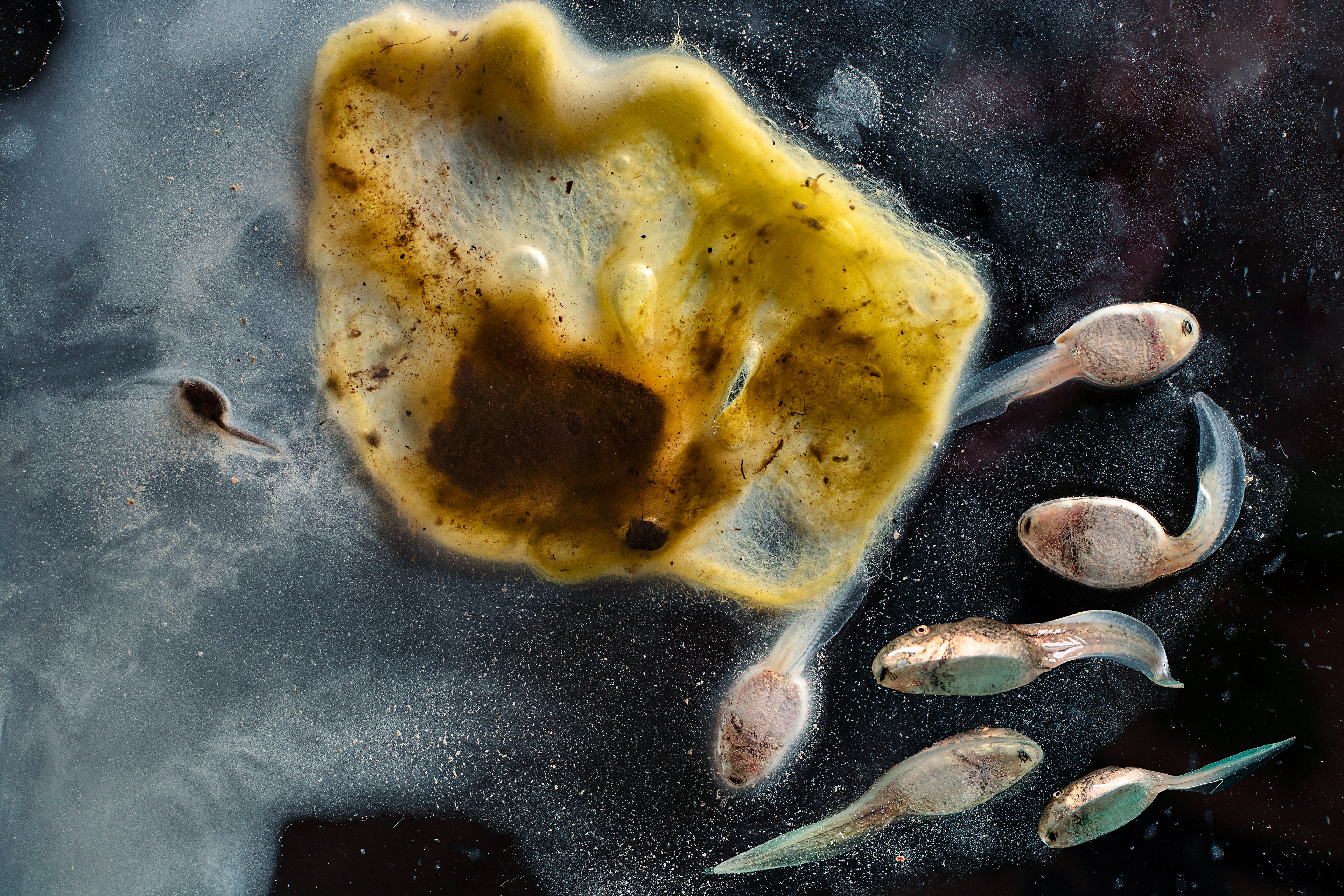
FROGS
Frog development is an excellent example of the concept of metamorphosis, demonstrating how an organism can undergo profound physical changes to adapt to different environments and stages of life.
Development of Limbs: As the tadpole grows, it undergoes metamorphosis, a process where its body undergoes significant changes. The hind legs develop first, followed by the forelegs.
Tail Reduction: The tadpole's tail begins to shorten as it is absorbed by the body.
Lung Development: Lungs develop, allowing the frog to breathe air, while the gills are gradually absorbed.
Dietary Shift: The tadpole's diet changes as its digestive system transforms from herbivorous to omnivorous, preparing it to eat insects and other small animals.
There are over 7,000 species of frogs, making them one of the most diverse groups of vertebrates. They are found on every continent except Antarctica.
Frogs are known for their remarkable jumping abilities. Some species can leap up to 20 times their own body length, which is equivalent to a human jumping over a 30-story building.
Male frogs are known for their loud and often complex calls, which they use to attract mates. Different species have distinct calls, and some frogs can even change the pitch of their calls depending on the situation.
Frogs play significant roles in various cultures and mythologies. In Ancient Egypt, they symbolized fertility and rebirth, while in Chinese culture, they are associated with good fortune and prosperity.
Frogs are highly sensitive to environmental changes, making them important indicators of ecosystem health. Pollution, habitat destruction, and climate change can have severe impacts on frog populations, which can signal broader environmental issues.


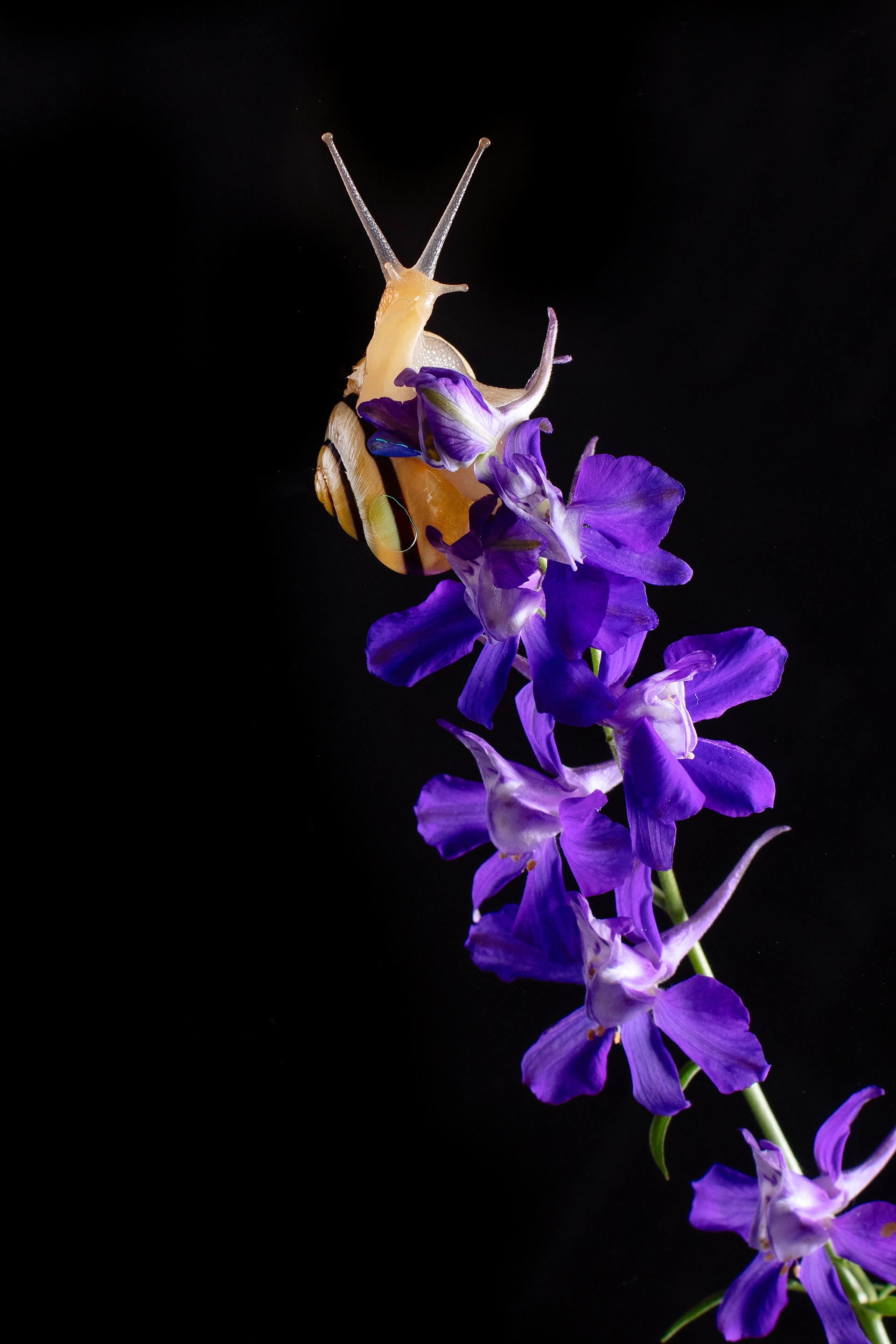
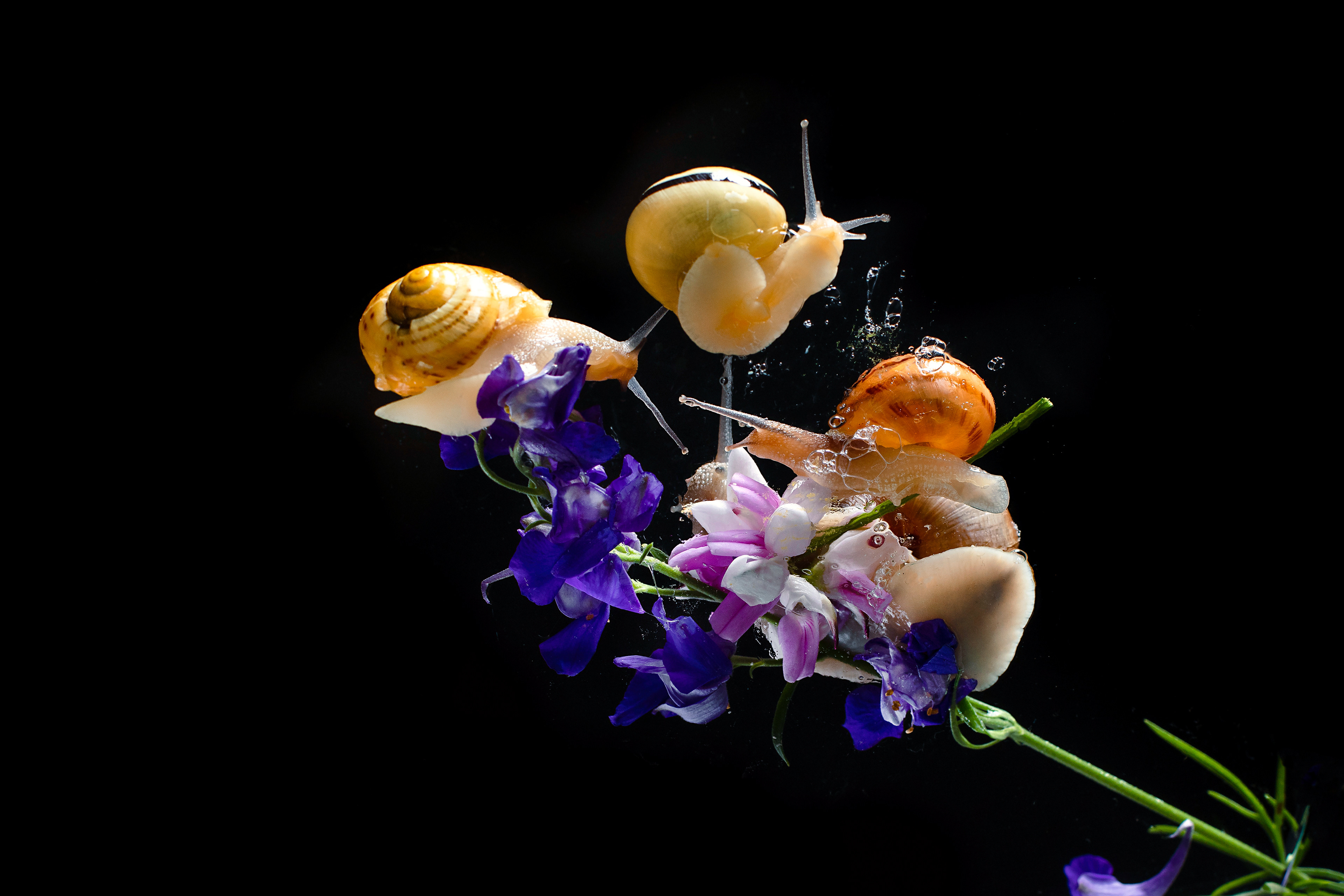
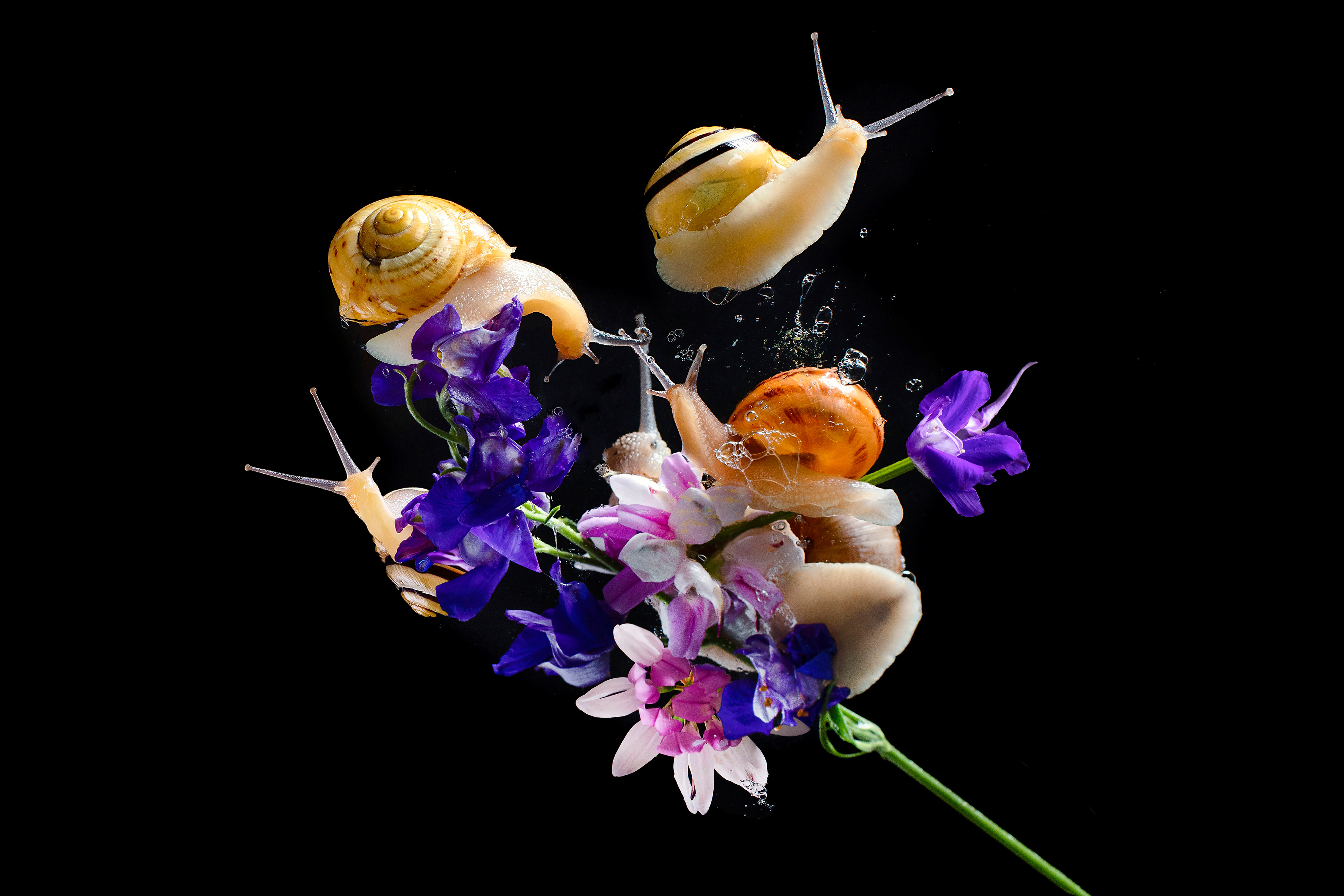
SNAILS
Here are some lesser-known and interesting facts about snails:
Sleep Cycles: Snails can sleep for several hours at a time, but their sleep cycles can span up to three years if the weather is not favorable.
Teeth: Snails have thousands of tiny teeth located on a ribbon-like tongue called a radula. Some species have up to 14,000 teeth!
Speed: Snails are incredibly slow movers, with an average speed of around 0.03 miles per hour.
Shell Growth: A snail's shell grows with them throughout their life. The shell is made of calcium carbonate and grows in a spiral shape.
Reproduction: Many snails are hermaphrodites, meaning they have both male and female reproductive organs, allowing them to mate with any adult of their species.
Sense of Smell: Snails rely heavily on their sense of smell to find food, as their vision is quite poor.
Habitat Diversity: Snails can be found in a wide range of habitats, from deep oceans to deserts, showing their incredible adaptability.
Lifespan: While many people think of snails as having short lives, some land snails can live up to 25 years in the wild.
Communication: Snails use chemical signals, known as pheromones, to communicate with each other, especially during mating seasons.
Defense Mechanisms: Some species of snails can produce a noxious or toxic mucus as a defense mechanism against predators.



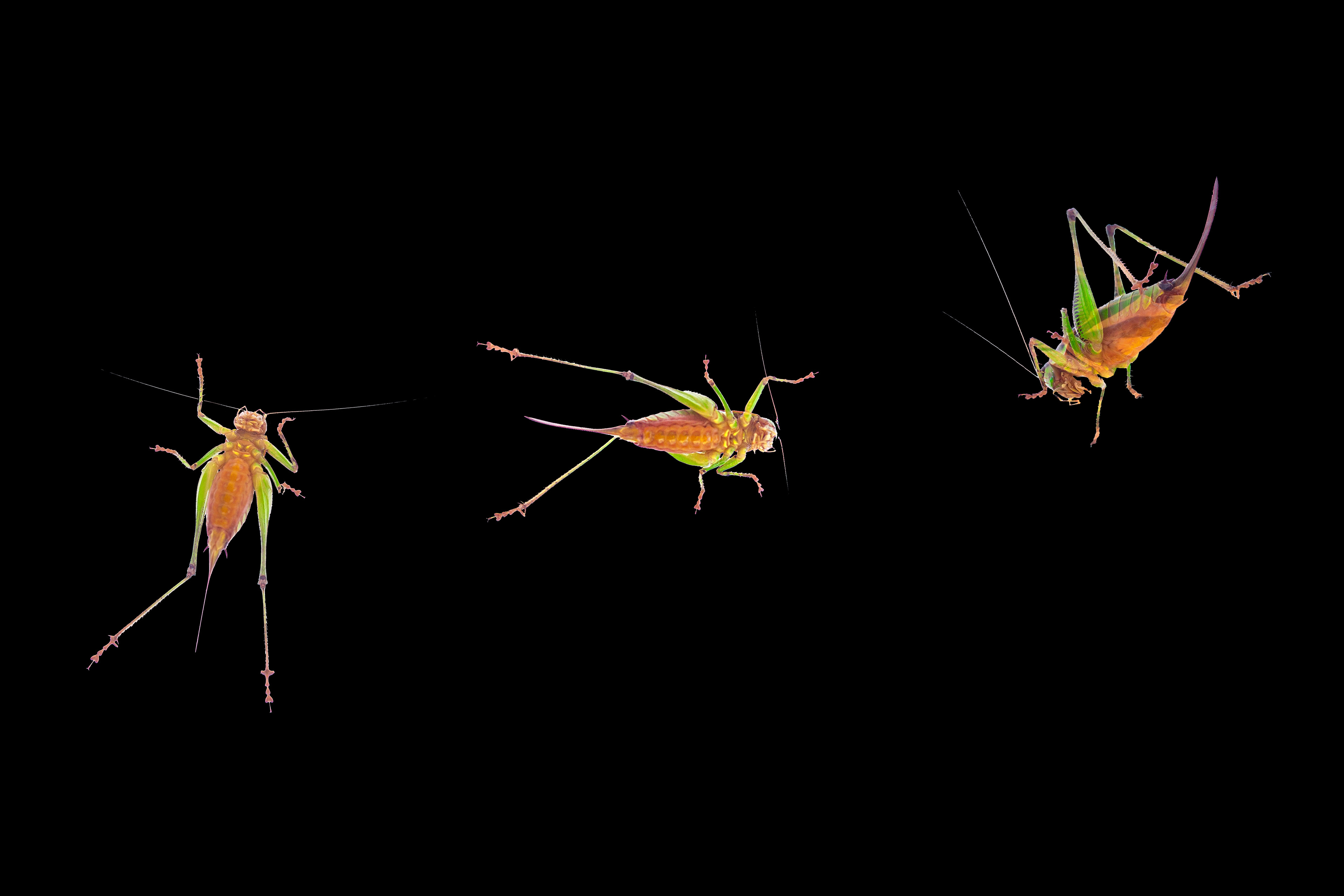
GRASSHOPPERS
Interesting facts about grasshoppers:
Ancient Insects: Grasshoppers have been around for over 250 million years, dating back to the Triassic period.
Variety of Species: There are about 11,000 known species of grasshoppers worldwide.
Powerful Legs: Grasshoppers have strong hind legs that allow them to leap up to 20 times their own body length.
Unique Ears: Grasshoppers have ears located on their abdomen, specifically on the first segment, called the tympanum.
Plant Diet: Most grasshoppers are herbivores, primarily eating leaves, flowers, stems, and seeds.
Sound Production: Grasshoppers produce sound (stridulation) by rubbing their hind legs against their wings to attract mates or deter predators.
Colorful Variety: Grasshoppers come in various colors, which can help with camouflage or warning predators of their potential toxicity.
Locusts: Certain species of grasshoppers can transform into locusts under specific environmental conditions, leading to swarming behavior and causing significant agricultural damage.
Metamorphosis: Grasshoppers undergo incomplete metamorphosis, developing through egg, nymph, and adult stages without a pupal stage.
Flight Ability: Some grasshopper species can fly long distances, aided by their large wings.

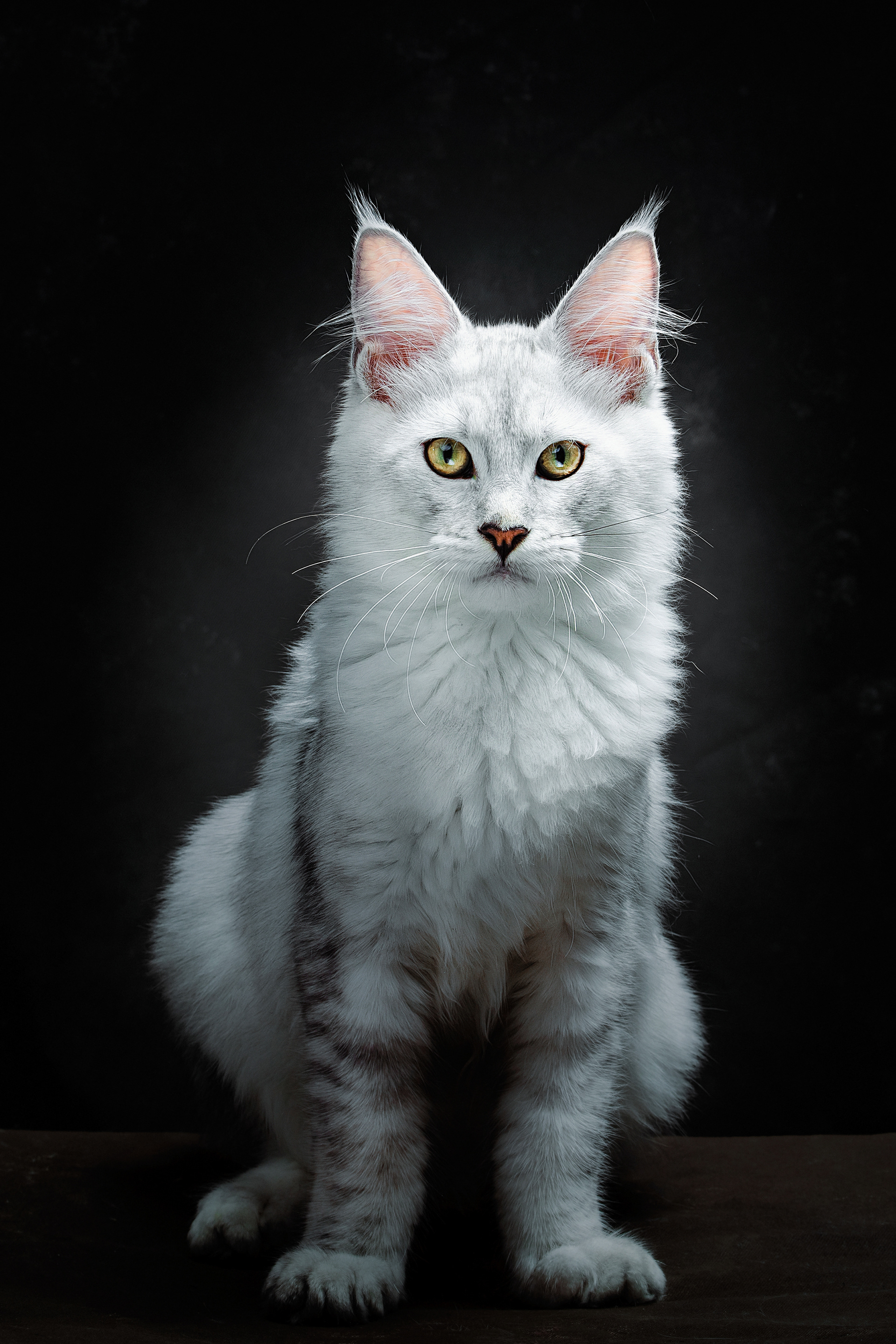
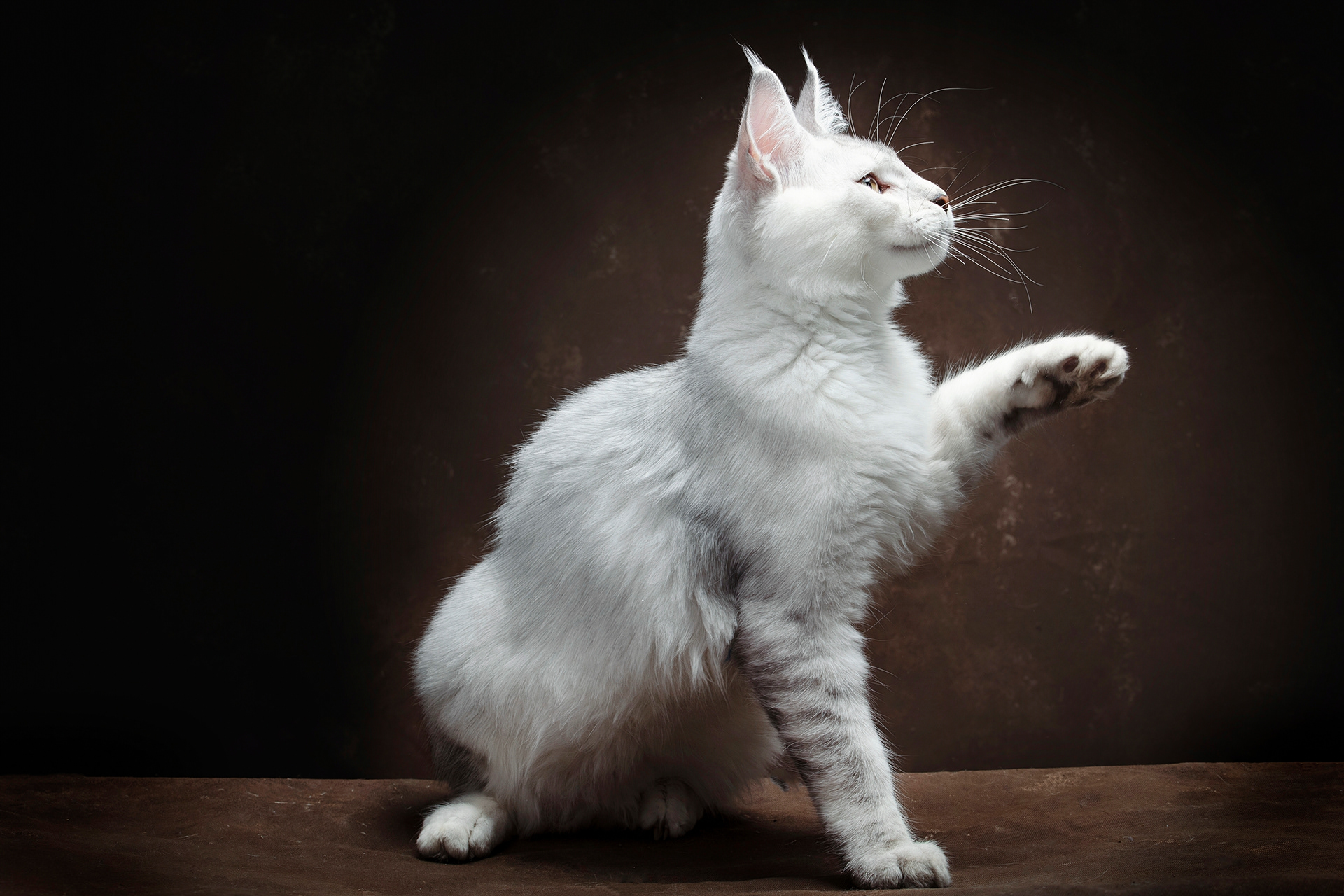
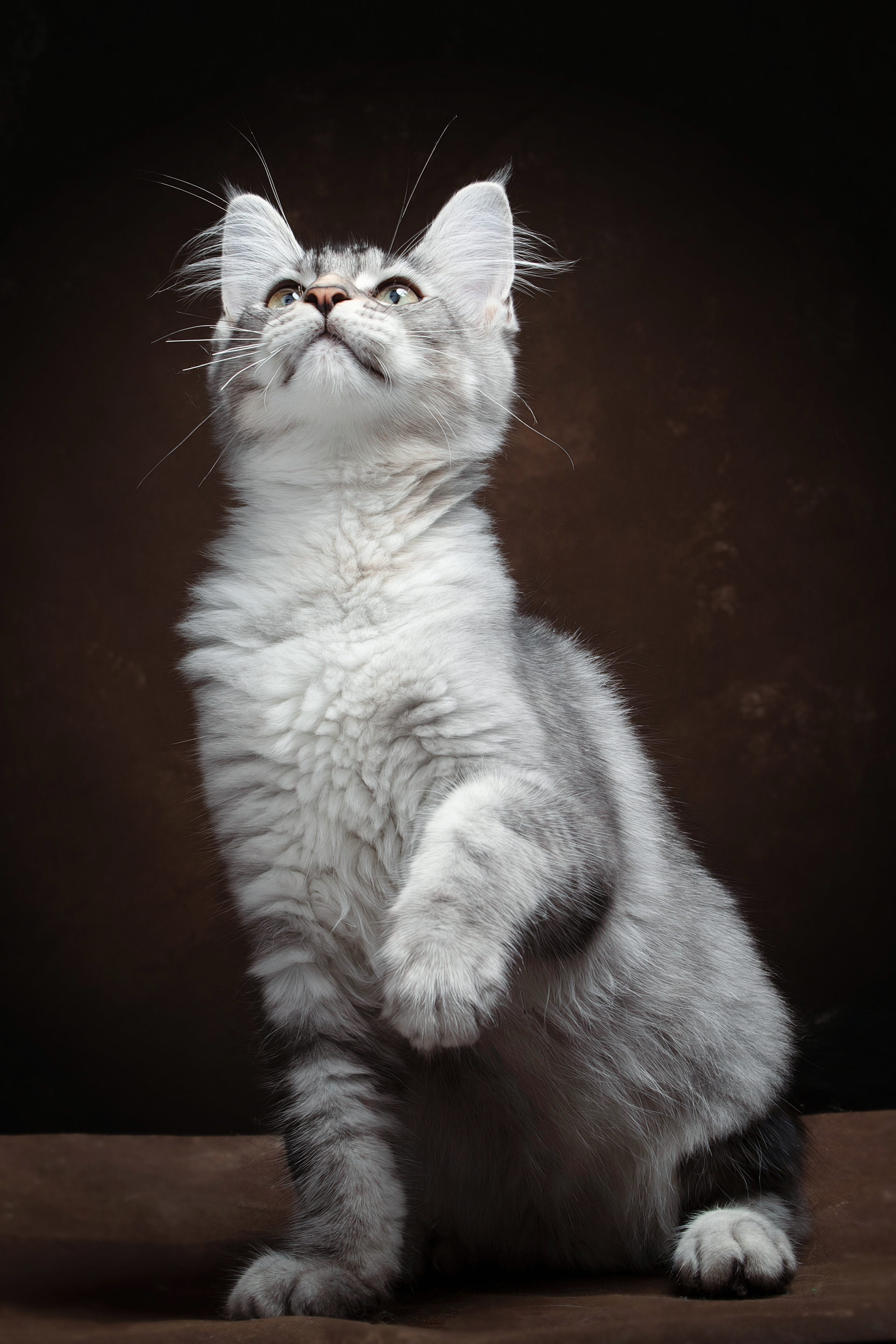
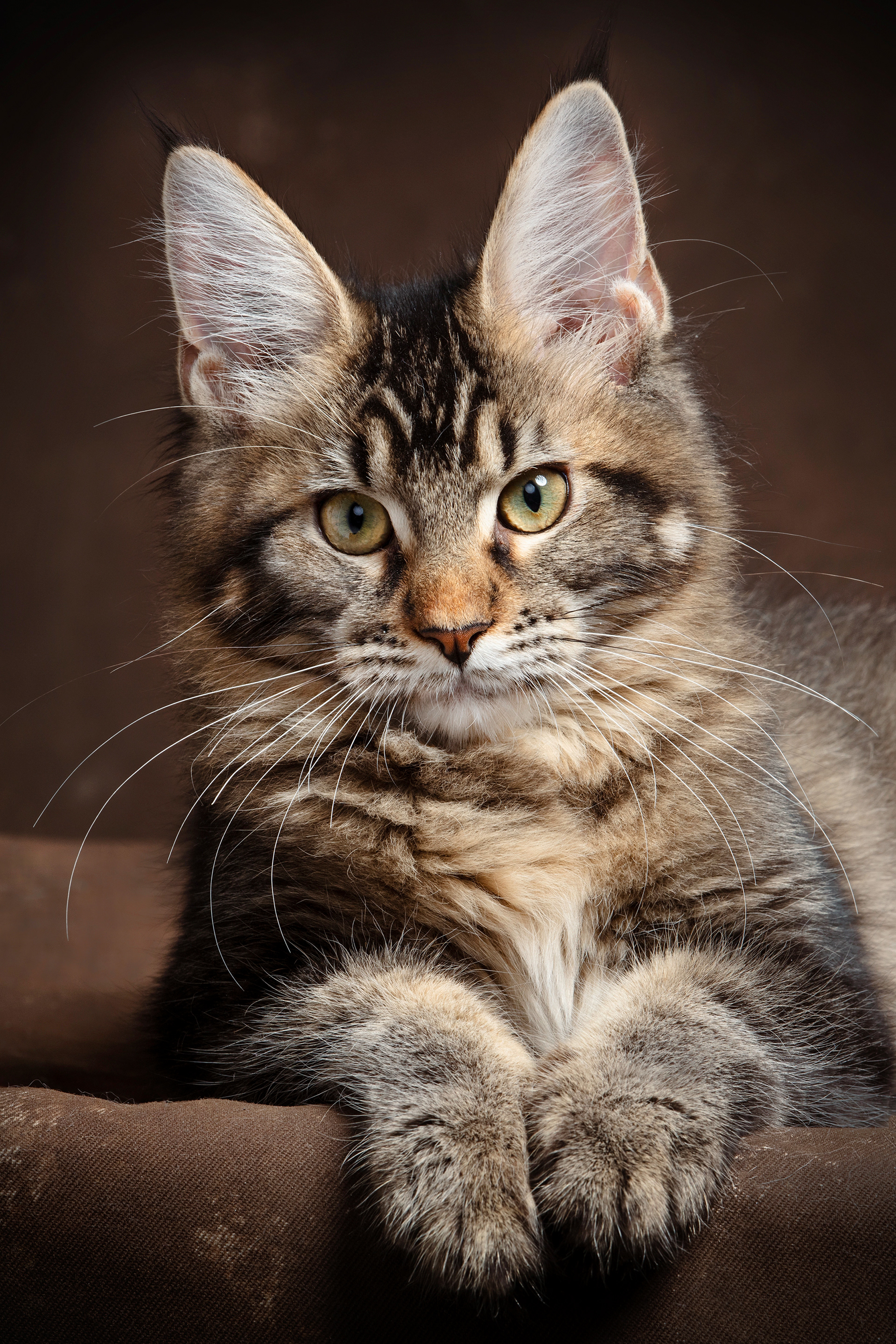
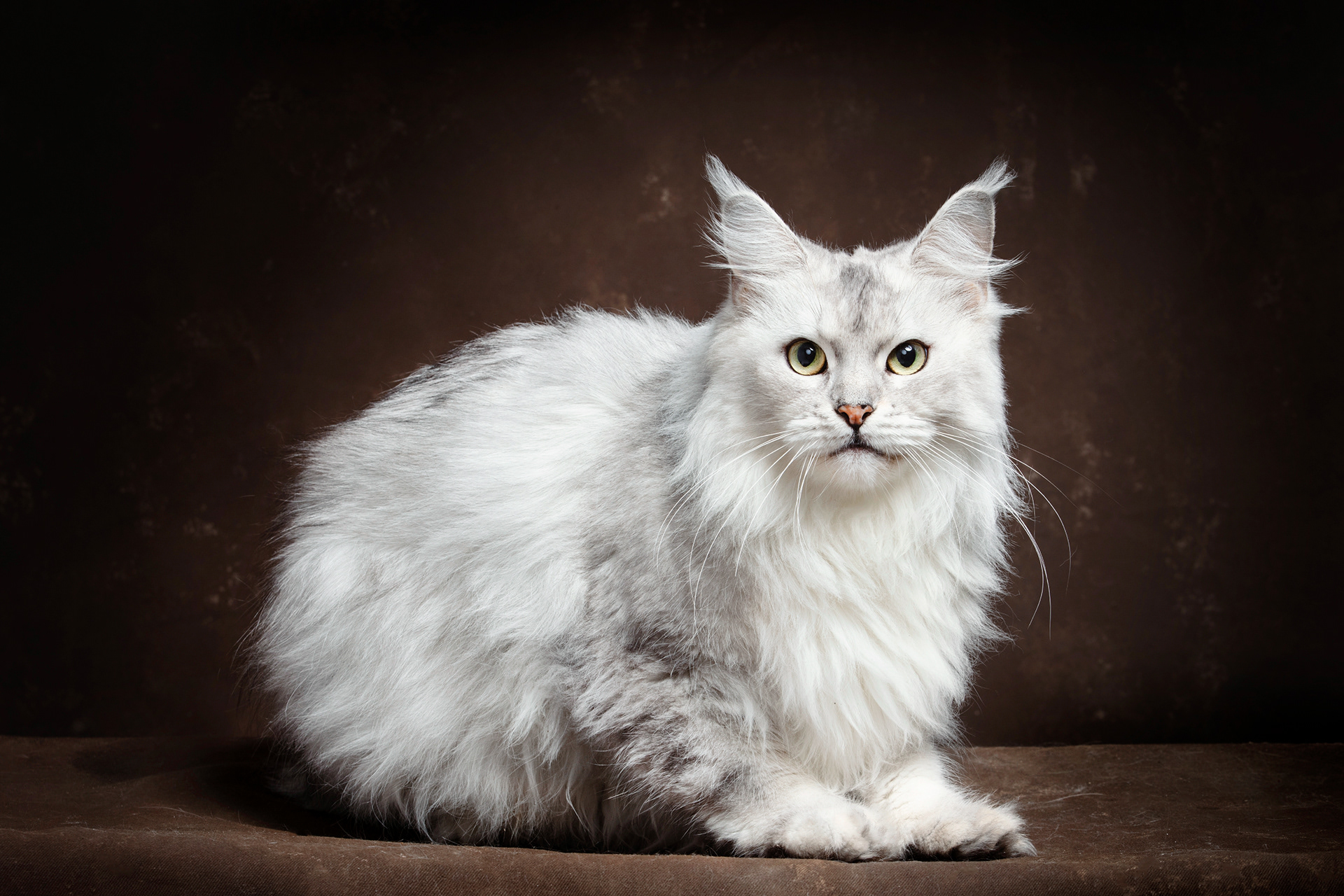
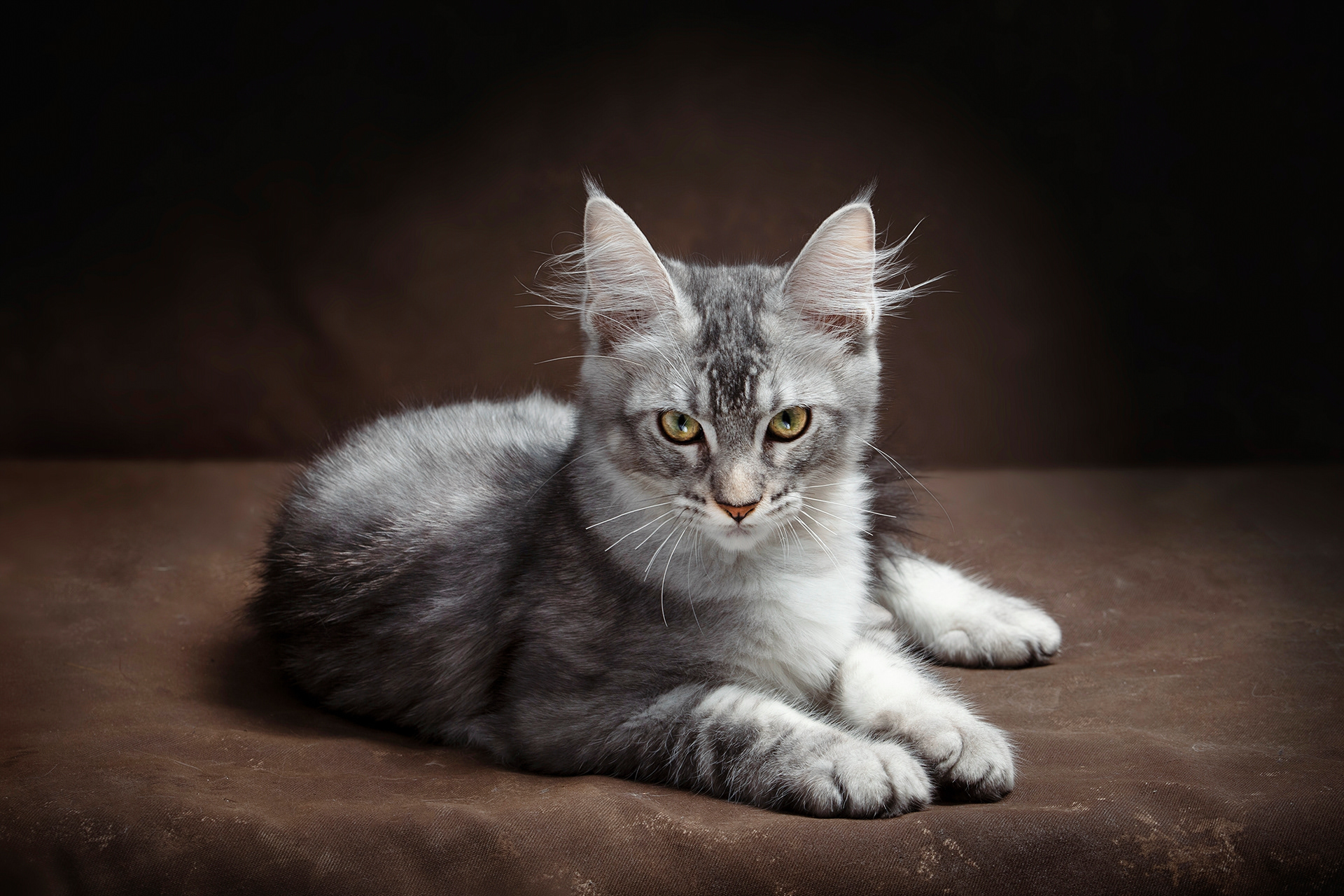
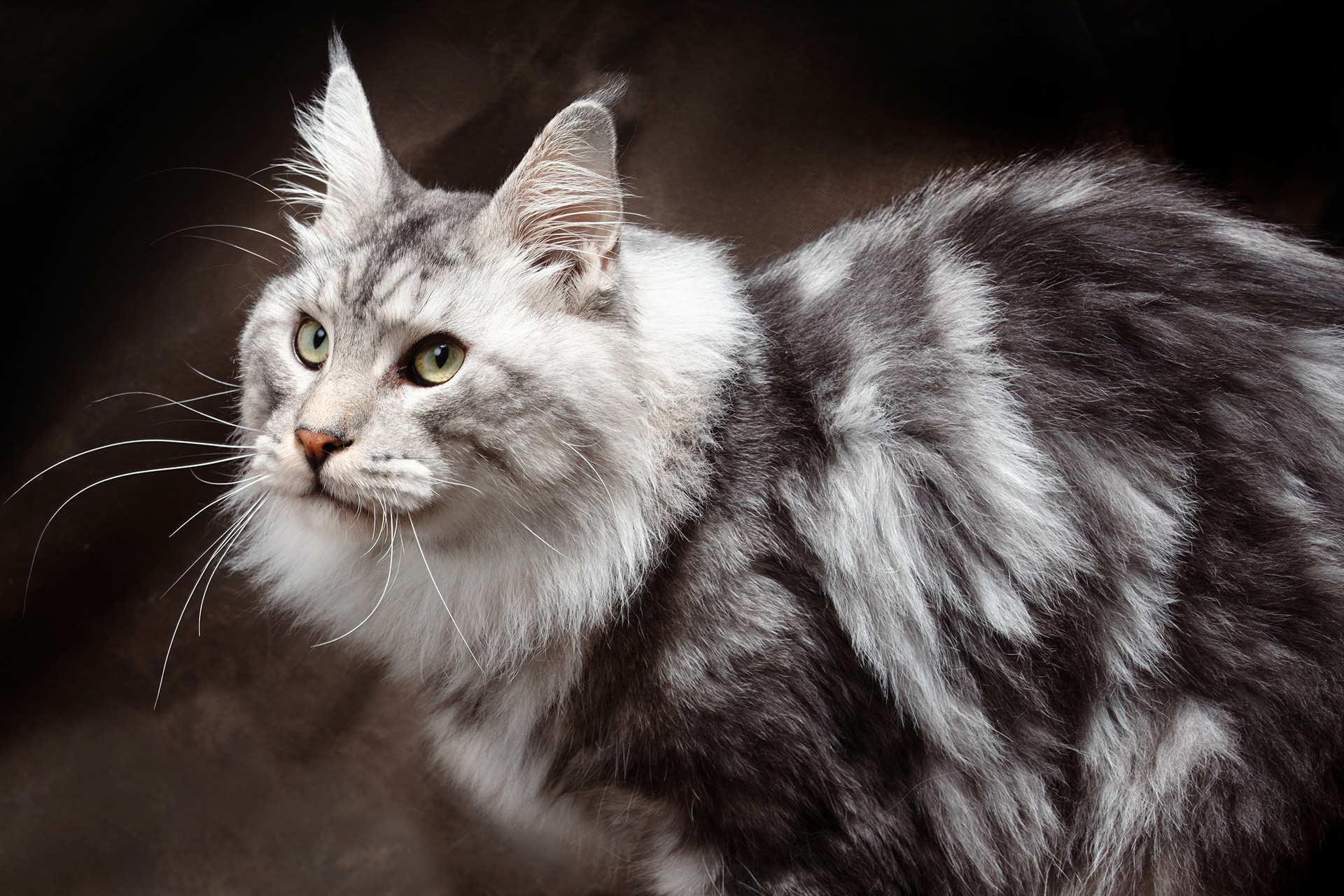
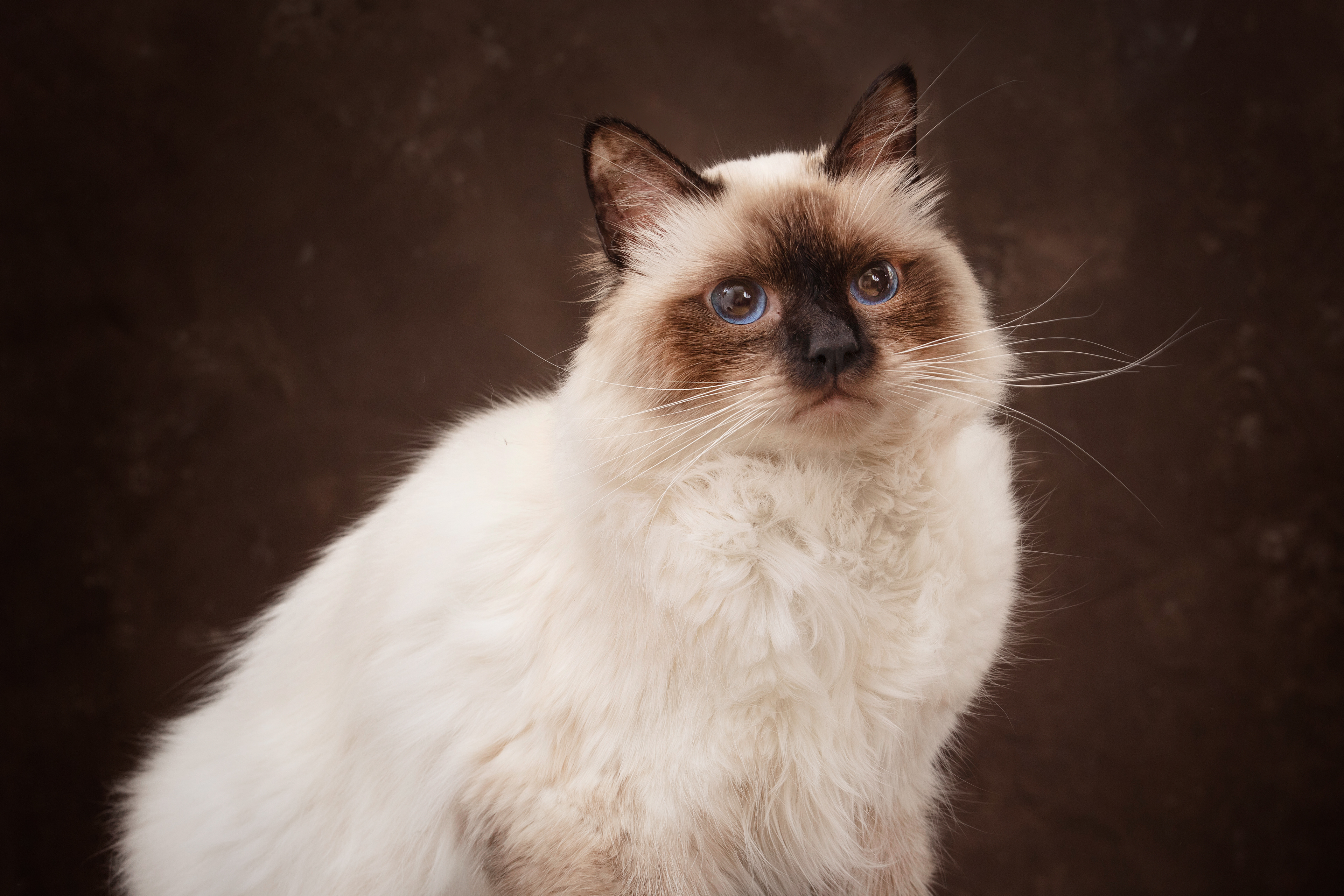
CATS
Cat photography can be both fun and challenging because capturing a cat's personality and beauty requires patience, timing, and the right techniques.







